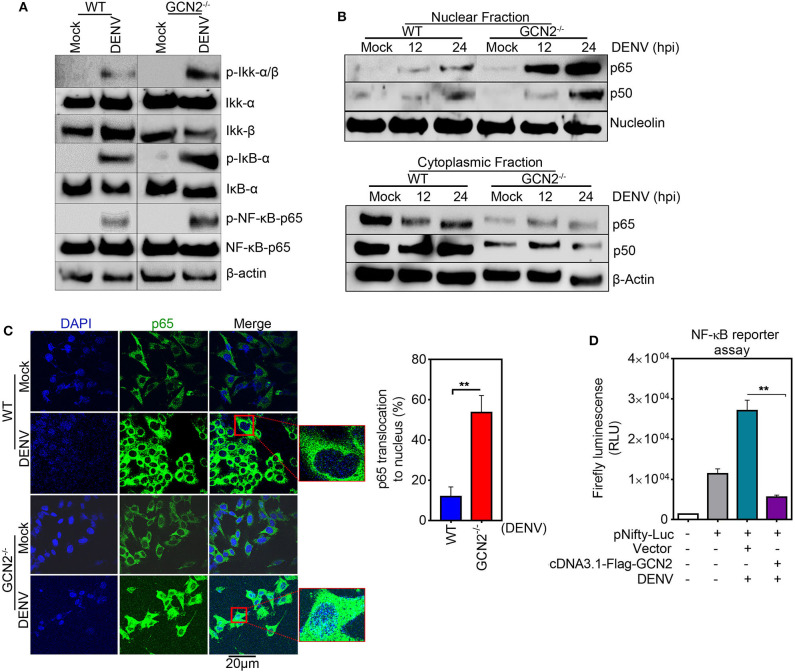
Figure 4.
GCN2 interferes with DENV induced COX-2 signaling by counteracting the activation of NF-κB pathway. (A) WT and GCN2−/− MEFs were mock infected or infected with DENV-2 (moi 3) for 24 h and examined for the expression of p-IKK-α/β, IKK-α, IKK-β, p-IKB-α, IKB-α, p-NF-κB-p65, and NF-κB-p65 through immunoblotting. (B) Immunoblot analysis of p65 and p50 accumulation in nuclear and cytoplasmic fraction of DENV-2 (moi 3) infected WT and GCN2−/− MEFs. (C) Confocal microscopy image showing the nuclear translocation of p65 in DENV-2 (moi 3) infected WT and GCN2−/− MEFs 24h post infection. Bar graph represents quantification of percentage of p65 translocation using Image J (NIH) software. Data shown is mean ± SEM from 10 different fields of three independent experiments (D) Firefly luminescence levels in HepG2 cells co-transfected with NF-κβ-responsive plasmid (pNifty-Luc) and pcDNA3.1-Flag-GCN2 plasmid or vector control for 36 h followed by DENV-2 (moi 3) infection for further 24 h. Graph represents data as mean ± SEM from two independent experiments performed in triplicates. **P < 0.01 was considered significant. Statistical analysis was done using two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test.