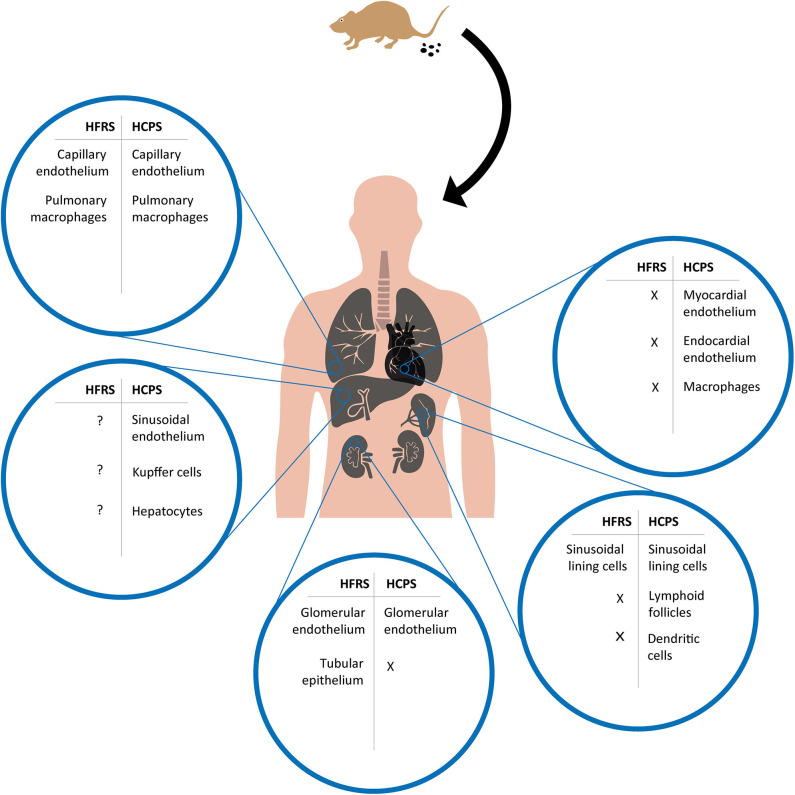
Figure 2.
Overview of cell tropism during HFRS and HCPS based on human and experimental disease models. After a human host is infected by inhalation of virus containing aerosolized excreta of an infected rodent, orthohantavirus is able to reach multiple organs and infect different cell types. Potentially infected cell types during HFRS and HCPS are compared for major organs in which viral antigens have been detected in human tissues or experimental disease models; lungs, heart, kidneys, liver, and spleen. X = absence of viral antigen; ? = viral antigen presence not specified.