FIGURE 2.
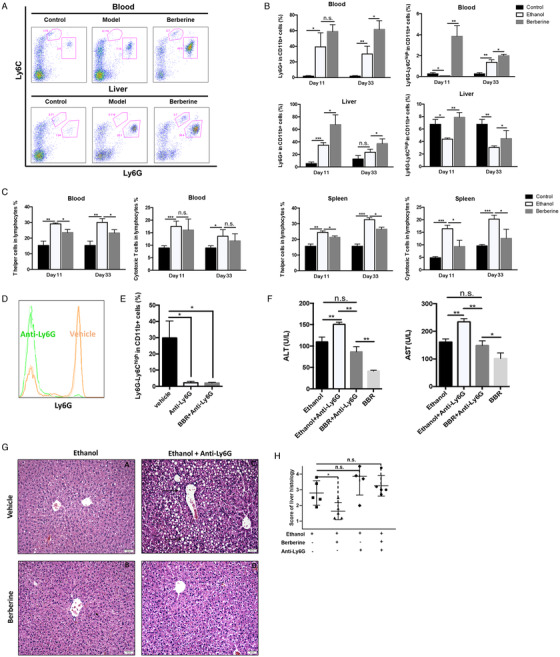
Berberine mediated the increase of G‐MDSC‐like cells to protect liver from alcohol‐induced injury. The populations of G‐MDSC‐like cells, M‐MDSC, or T cells in blood, liver, and spleen of mice were determined by flow cytometer. Berberine significantly promoted the increase of G‐MDSC‐like cells in liver and blood. A, The representative histogram images and quantification (b) of flow cytometric analyses of G‐MDSC‐like cells and M‐MDSC in blood and liver of mice of control group, ethanol model group, and berberine group. C, Quantification of flow cytometric analyses of T helper and cytotoxic T cells in blood and spleen of mice. Anti‐ly6G antibody or vehicle was treated to ethanol‐fed mice (N = 5 for each group). D, Representative histogram images and quantification (E) of flow cytometric analyses of G‐MDSC‐like cells in liver of mice treated with anti‐Ly6G or vehicle. F, Serum ALT and AST level of mice treated with anti‐Ly6G or vehicle. G, Representative H&E staining images of liver of mice treated with anti‐Ly6G or vehicle and scoring of histological damage (H). The lipid deposition and steatosis are indicated by arrows. * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001; n.s., not significant; BBR, berberine
