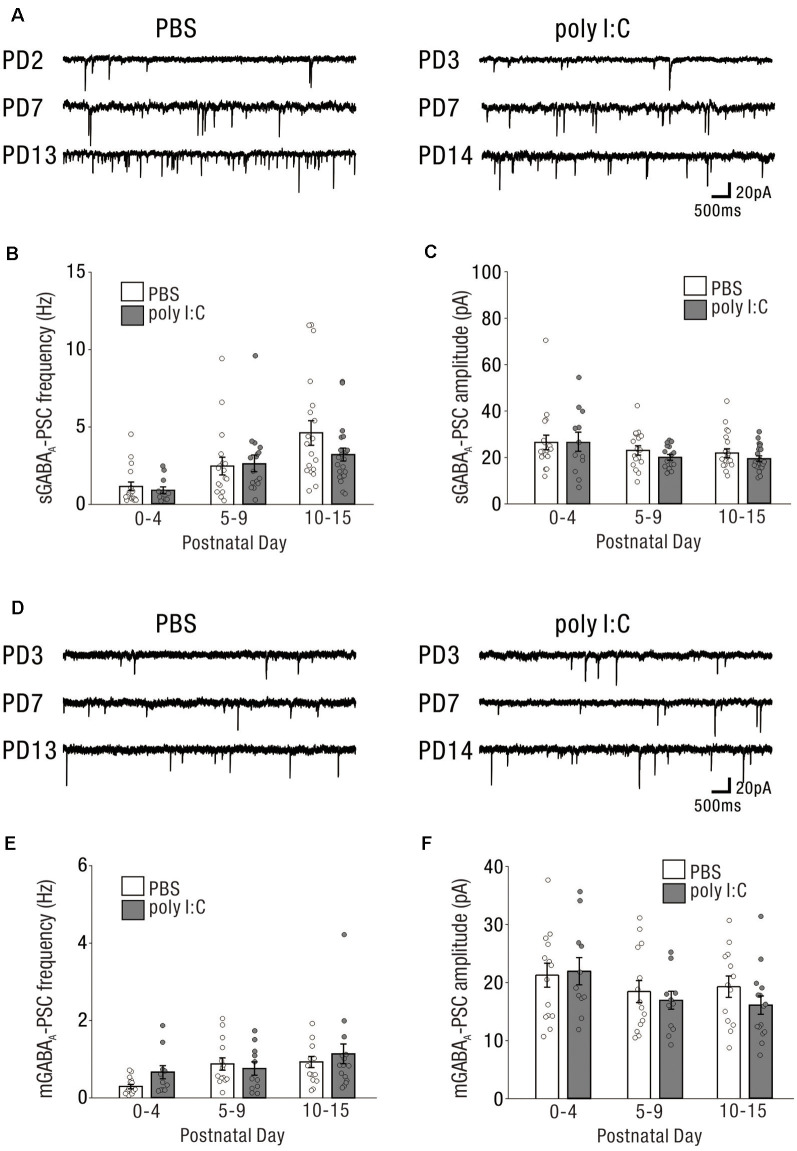
Figure 4.
The impact on GABAergic drive and synaptic inputs onto CA1 pyramidal cells in the early postnatal period by prenatal poly I:C treatment are undetected. (A) Representative data of sGABAA-PSCs recorded from a CA1 pyramidal cell of a PBS-treated mouse (left) and poly I:C-treated mouse (right) in each PD during the neonatal period. (B,C) There were no significant differences in sGABAA-PSC frequency and amplitude between PBS-treated and poly I:C-treated mice. (D) Representative data of mGABAA-PSCs recorded from a CA1 pyramidal cell of a PBS-treated mouse (left) and poly I:C-treated mouse (right) in each PD during the neonatal period. (E,F) There were no significant differences in mGABAA-PSCs frequency and amplitude between PBS-treated and poly I:C-treated mice. Poly I:C, polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidilic acid; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; mGABAA-PSC, miniature GABAA receptor-mediated postsynaptic current; sGABAA-PSC, spontaneous GABAA receptor-mediated postsynaptic current.