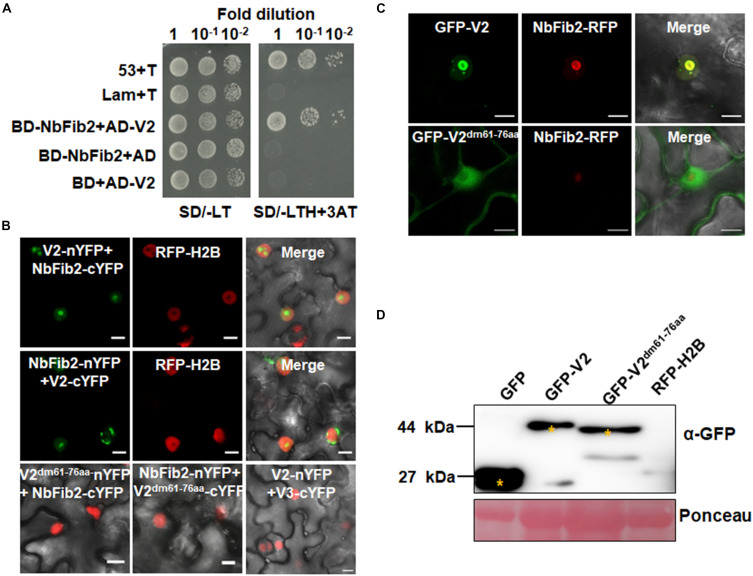
FIGURE 2.
V2 interacts with NbFib2. (A) Yeast two-hybrid assay showing the interaction between V2 and NbFib2 in yeast cells. Full-length NbFib2 was expressed as GAL4 DNA-binding domain fusion (BD, bait) and V2 was expressed as GAL4 activation domain fusion (AD, prey) in yeast cells of the strain Y2H Gold. The interaction of p53 and T was used as a positive control, and cotransformation of Lam and T was used as a negative control. Growth on the plates lacking leucine and tryptophan (SD/-LT) indicates successful transformation of both prey and bait vectors, respectively. Interaction between NbFib2 and V2 is indicated by growth of yeast cells on media also lacking histidine supplementing with 5 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (SD/-LTH + 3-AT). (B) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay (BiFC) assay showing the interaction between NbFib2 and V2 in plant cells. Constructs containing N-terminal YFP fusion (nYFP) and C-terminal YFP fusion (cYFP) fusions were infiltrated into RFP-H2B plant leaves. Combinations of BiFC constructs are shown at the top of each panel. Images were taken using a Zeiss LSM 880 confocal laser scanning microscope at 48 hpi. Reconstituted YFP signals resulting from V2-NbFib2 interaction are displayed as a false-green color. RFP-H2B served as a nuclear marker. Note that deletion of the predicted nuclear localization signal (from amino acid 61–76) of V2 abolishes its interaction with NbFib2. (C) Colocalization analysis of NbFib2 with V2 and V2 mutant in the epidermal cells of N. benthamiana by Zeiss LSM 880 confocal laser scanning microscope at 36 hpi. At least 60 cells from three repeats were examined. Scale bars correspond to 10 μm. (D) Immunoblot of proteins from RFP-H2B plant leaves infiltrated with construct as indicated using anti-GFP antibody. Ponceau staining of the large subunit of Rubisco serves as a loading control.