Figure 1.
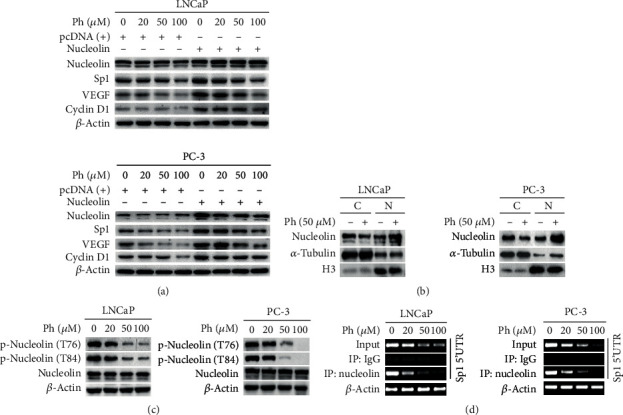
Phloretin decreased Sp1 level by inhibiting nucleolin binding to 5′-UTR of Sp1 mRNA via decreasing the levels of p-Nucleolin(T76 and T84) and regulating the nuclear and cytoplasmic distribution of nucleolin. (a) Cells were treated with different concentrations of phloretin and/or cotransfected with nucleolin expression plasmid, and then cells were harvested for western blotting assay to detect the levels of nucleolin, Sp1, VEGF, and Cyclin D1. (b) LNCaP and PC-3 cells were treated with/without phloretin (50 μM) for 24 h and then harvested for nucleus and cytoplasm separation experiment and western blot assays to check the distribution of nucleolin in the cytoplasm (C) and the nucleus (N). (c) LNCaP and PC-3 cells were treated with phloretin (0, 20, 50, and 100 μM) for 24 h and then harvested for western blot assay to check the levels of nucleolin, p-Nucleolin(T76), p-Nucleolin(T84), and β-actin (loading control). (d) LNCaP and PC-3 cells were treated with phloretin (0, 20, 50, and 100 μM) for 24 h and then collected for RT-PCR (β-actin as internal control and Sp1 5′-UTR as input) and RNA-IP with IgG and anti-nucleolin antibody to check the binding levels of nucleolin to 5′-UTR of Sp1 mRNA. The RT-PCR products of mRNAs (including internal control β-actin mRNA, input Sp1 mRNA, and nucleolin-bound Sp1 mRNAs in the products of RNA-IP with IgG and anti-nucleolin antibody) were assayed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
