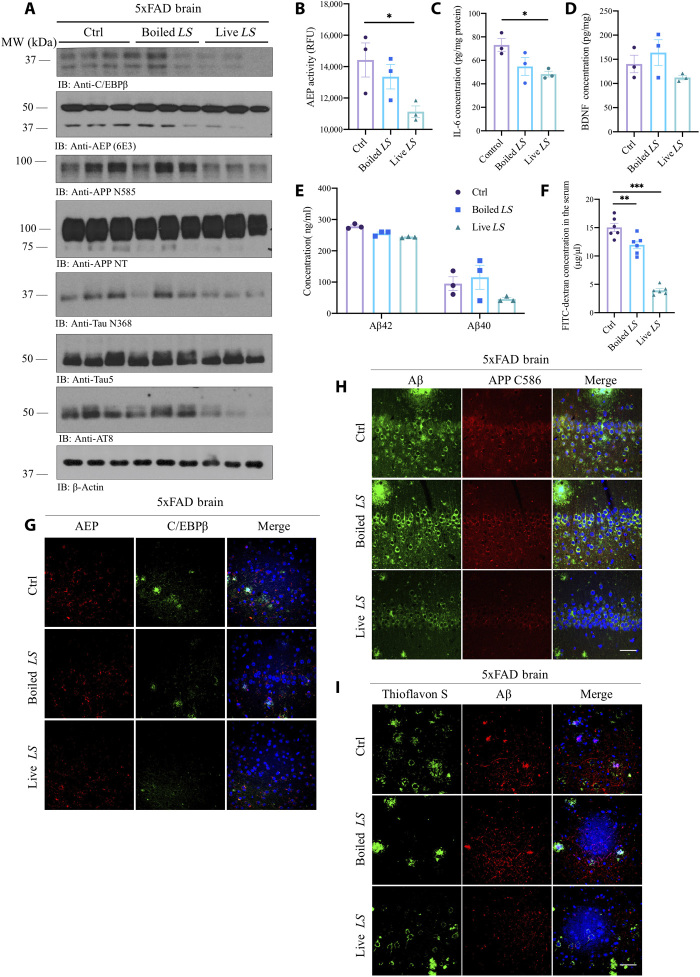
Fig. 7. R13-induced probiotic L. salivarius suppresses C/EBPβ/AEP signaling in the brain of 5xFAD mice, decreasing gut leakage.
(A) Immunoblot showing p-C/EBPβ, C/EBPβ, AEP, APP, and Tau expression and processing in the mouse brains. LS, L. salivarius. (B) AEP activity assay in the brain lysates from 5xFAD treated with live L. salivarius, boiled L. salivarius, or control. Data represent the means ± SEM; representative data of three samples; *P < 0.05 compared with control, one-way ANOVA. (C) Live L. salivarius treatment decreased IL-6 concentrations in the mouse brains. Data represent the means ± SEM; representative data of three samples; *P < 0.05 compared with control, one-way ANOVA. (D) BDNF concentrations in the brains from 5xFAD treated with live L. salivarius, boiled L. salivarius, or control. Data represent the means ± SEM; representative data of three samples. (E) Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 concentrations in 5xFAD mice treated with live L. salivarius, boiled L. salivarius, or control, respectively. Data represent the means ± SEM; representative data of three samples. (F) GI permeability barrier defect, as determined by FITC-dextran translocation in 5xFAD mice treated with live L. salivarius, boiled L. salivarius, or control. Data represent the means ± SEM; representative data of six samples; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, compared with control, one-way ANOVA. (G to I) IF staining of C/EBPβ and AEP; Aβ/APP C586 and Aβ/ThS on the brain sections from 5xFAD mice treated with live L. salivarius, boiled L. salivarius, or control. Scale bars, 20 μm.