Fig. 4. Coding and noncoding mutations affect distinct sets of genes.
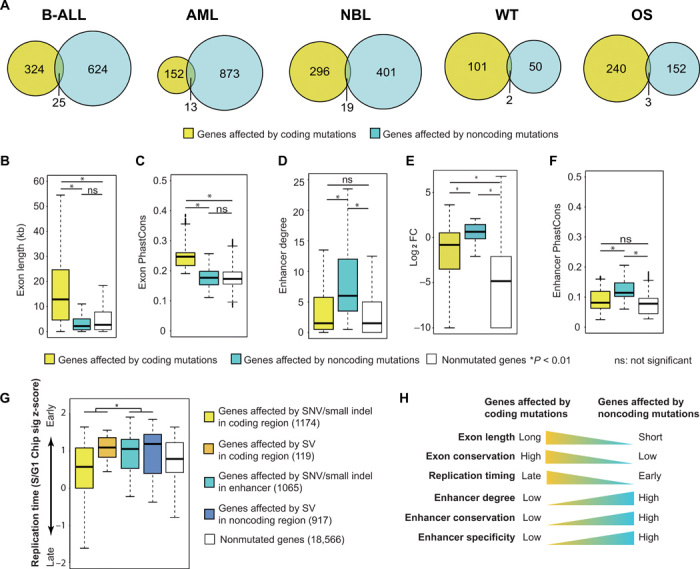
(A) Venn diagrams of genes affected by recurrent coding and noncoding mutations in five cancer types. (B to G) Features of genes affected by coding and noncoding mutations and genes without any mutation: gene exon length (B), exon conservation level measured by PhastCons score (C), enhancer degree (number of enhancers regulating a promoter) (D), gene expression specificity measured by fold change (FC) of average expression in a given cancer type compared to that of all five pediatric cancer types (E), enhancer conservation level measured by PhastCons score (F), and replication timing (G). (H) Summary of different genomic features for the genes affected by coding and noncoding mutations. P values of one-sided t test are shown (n = 21,841).
