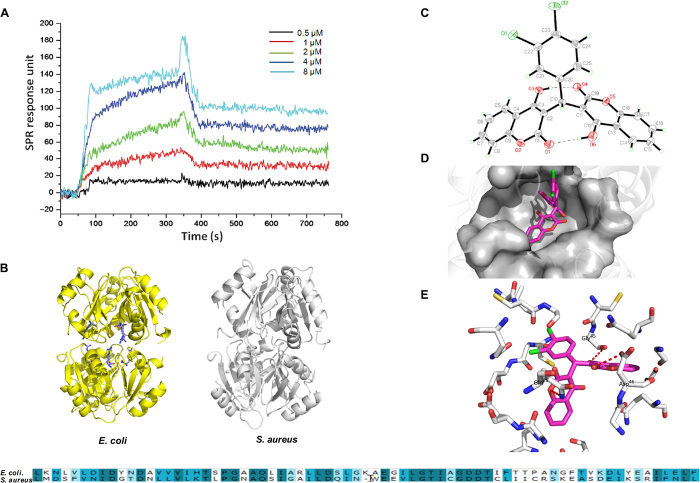
Fig. 4. The binding affinity and site of DCH to bacterial ArgR.
(A) Relative RU was induced by DCH in dose-dependent model from 0.5 to 8 μM. (B) Homology model building of S. aureus ArgRC (right) was performed according to the sequence alignment with the E. coli ArgRC (left); the sequence alignment result of ArgR C-terminal residues between E. coli and S. aureus is shown in bottom. (C) Crystal structure diagram of the asymmetric unit including the atomic numbering scheme of compound DCH. (D) Overview of the docked pose showed that DCH shared a very similar binding pocket to arginine in the ArgRC. (E) The 3D schematic showed two noticeable interactions between the benzene rings of DCH and two amino acids (GLN25 and ASP46) of ArgRC in the active site.