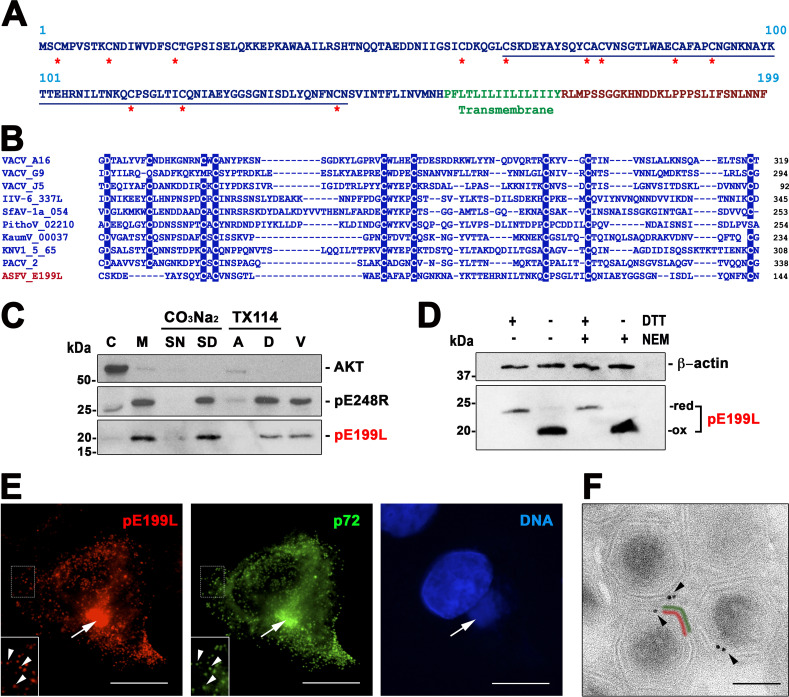
FIG 1.
ASFV transmembrane protein pE199L. (A) Amino acid sequence of pE199L protein (BA71V strain). The putative cytosolic, cystein-rich (asterisks) N-terminal region is indicated in blue, whereas the putative transmembrane domain and the short C-terminal region are indicated in green and red, respectively. (B) Multiple-sequence alignment of the most highly conserved region (underlined in panel A) of the N-terminal region of pE199L with possible NCLDV orthologues identified in different virus families or groups as follows: poxviruses (VACV ORFs A16, G9, and J5), iridoviruses (IIV type 6, ORF IIV6-337L), ascoviruses (SfAV-1a, ORF 054), pithoviruses (PithoV ORF 02210), kaumoebaviruses (KaumV ORF 00037), mimiviruses (KNV1 type 5, ORF 65), and pacmanviruses (PACV, ORF 2). Amino acids identical in at least 80% of the selected 10 aligned sequences are highlighted. (C) Membrane association of pE199L protein. ASFV-infected cells were fractionated into cytosolic (C) and membrane/particulate (M) fractions, which were analyzed by Western immunoblotting with an anti-pE199L antibody. In addition, the membrane fraction was subjected to alkaline carbonate (pH 11.5) extraction and centrifugation or to temperature-induced phase separation after Triton X-114 extraction. Equivalent fractions of the supernatant (SN) and sediment (SD) obtained after carbonate extraction and of the aqueous (A) and detergent-rich (D) phases obtained after TX-114 extraction were analyzed as described above. Cytosolic marker AKT and membrane protein pE248R were also analyzed as controls. Purified ASFV particles (V) were also analyzed as indicated at the right of the immunoblots. Molecular masses (in kilodaltons) are indicated at the left of the blots, while the position of the pE199L band is indicated at the right. (D) pE199L forms intramolecular disulfide bonds. ASFV-infected Vero cell extracts were lysed under reducing (DTT) and nonreducing conditions in the presence or absence of the alkylating agent NEM. Protein pE199L was detected by Western blotting as described above. The positions of the bands corresponding to the oxidized (ox) and reduced (red) forms of pE199L are indicated on the right. Actin b was analyzed as a loading control. (E) Subcellular localization of pE199L. ASFV-infected cells were fixed at 18 hpi and immunolabeled with a rat antibody against pE199L (red) and MCP p72 (green). Nuclear and viral DNA was stained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). The arrows indicate colocalization at virus factories, whereas the arrowheads (insets) indicate colocalization at virus particles scattered throughout the cytoplasm. Bars, 5 μm. (F) Subviral localization of pE199L. ASFV-infected cells were fixed at 18 hpi and immunolabeled with a rat antibody against pE199L followed by an anti-rat antibody conjugated to 10-nm-diameter gold particles. Note that most of the gold particles present on intracellular viruses were associated with the inner envelope (red) beneath the outer protein capsid (green). Bar, 100 nm.