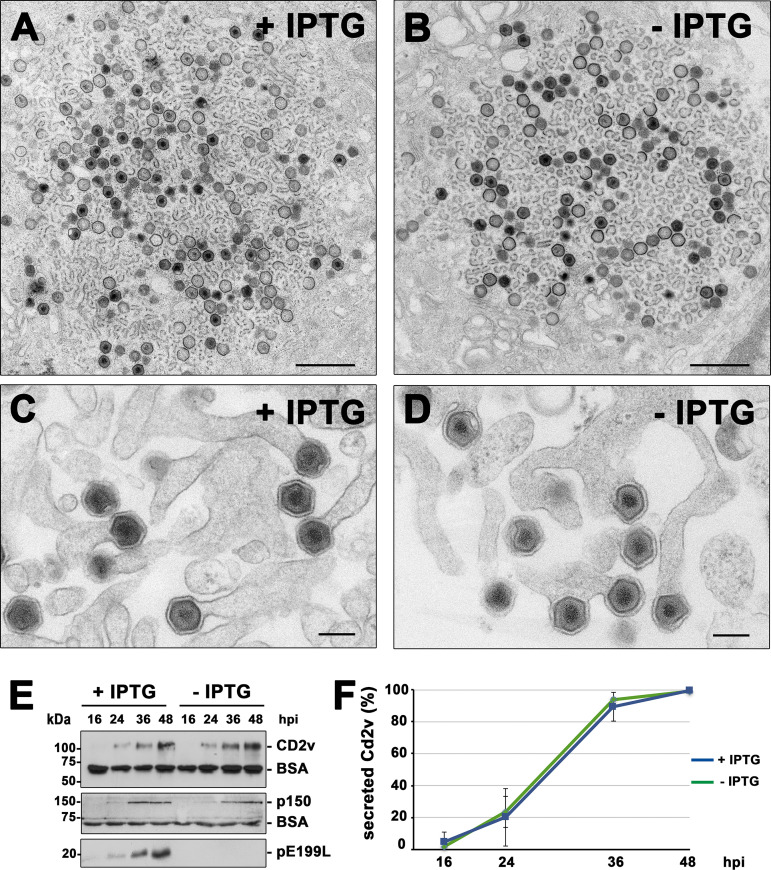
FIG 4.
Protein pE199L is not required for virus assembly and egress. (A to D) Transmission EM of ultrathin sections of vE199Li-infected Vero cells incubated for 18 h with (A and C) or without (B and D) IPTG. Note that the overall appearance of the cytoplasmic viral factories (A and B), with the presence of numerous precursor viral membranes as well as immature and mature icosahedral intracellular particles, was similar under both sets of conditions. As shown in panel D, defective vE199Li− particles apparently undergo normal budding at the plasma membrane, as occurs with the mature particles produced under permissive conditions (C). Bars, 1,000 nm (A and B) and 200 nm (C and D). (E) Supernatants from Vero cells infected with recombinant vE199Li in the presence (+) or absence (−) of IPTG were collected at the indicated times of infection and analyzed by immunoblotting for the outer viral envelope protein CD2v, the core shell protein p150, and the inner envelope protein pE199L. An antibody against BSA was used as a loading control. (F) Quantification by densitometry of the CD2v bands detected by immunoblotting as described for panel E. Data are expressed as percentages of secreted CD2v (means ± SD of results from triplicate samples) relative to that reached at 48 hpi in a vE199Li infection in the presence of IPTG. Data were normalized according to the levels of BSA detected under each set of conditions.