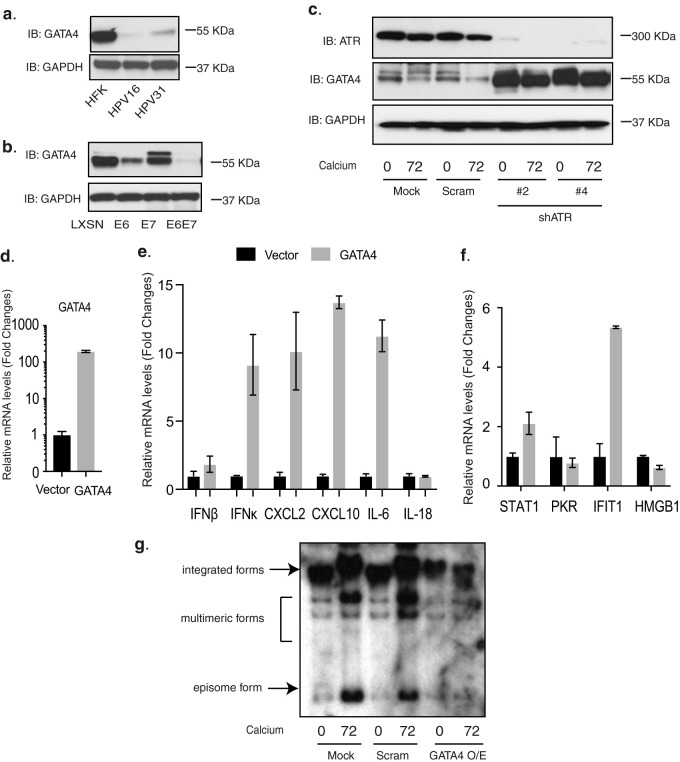
FIG 5.
Overexpression of GATA4 increases expression of inflammatory genes and IFN-κ in CIN612 cells. (a) Western blot analysis of GATA4 and GAPDH levels in HFK, HPV16, and HPV31 cells differentiated in high-calcium media for the indicated times (in hours). (b) Western blot analysis of GATA4 and GAPDH levels in HFK cells expressing LXSN vector, HPV31E6, HPV31E7, and HPV31E6/E7. (c) Western blot analysis of ATR, GATA4, and GAPDH levels in mock, scrambled control, and two stably selected ATR knockdown CIN612 cells upon differentiation in high-calcium media for 72 h. (d) RT-PCR analysis of GATA4 expression levels in CIN612 cells. (e) RT-PCR analysis of IFN-β, IFN-κ, CXCL2, CXCL10, IL-6, and IL-18 in GATA4-overexpressing CIN612 cells. (f) RT-PCR analysis of STAT-1, PKR, IFIT1, and HMGB1 in GATA4-overexpressing CIN612 cells. GAPDH was used as an internal control and for normalization of the data. Data are means ± standard errors. P value <0.05. (g) Southern blot analysis of HPV genome status in GATA4-overexpressing cells. Overexpression of GATA4 in HPV-positive cells leads to loss of episomes and cells with almost exclusively integrated genome copies (far two right lanes). All results are representative of observations from two or more independent experiments.