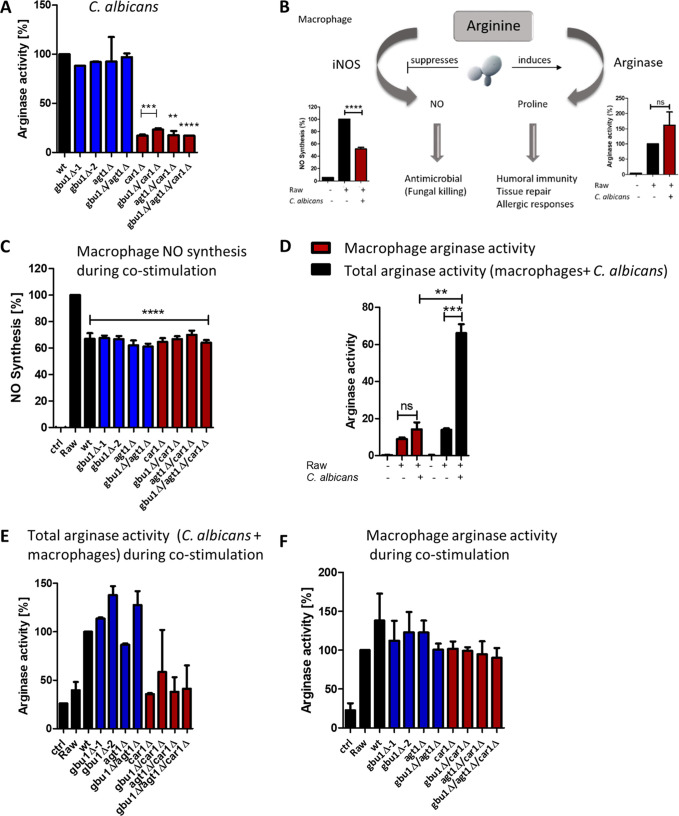
FIG 2.
Arginase activity in C. albicans ureohydrolase mutants plus arginase and iNOS activity during the macrophage interaction. (A) Arginase activity was determined in protein extracts isolated from C. albicans cultures grown in YPD. (B) Schematic model of how C. albicans might compete for arginine in competition with macrophages, leading to suppression of NO synthesis by inducing arginase activity (based on data from reference 32). (C) Macrophage NO synthesis following costimulation with C. albicans wild-type and ureohydrolase mutant strains. (D) Macrophage-derived or total (macrophage and C. albicans) arginase activity following costimulation with C. albicans wild-type cells. (E and F) Total (E) or macrophage-derived (F) arginase activity following costimulation with C. albicans wild-type and ureohydrolase mutant strains. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not statistically significant.