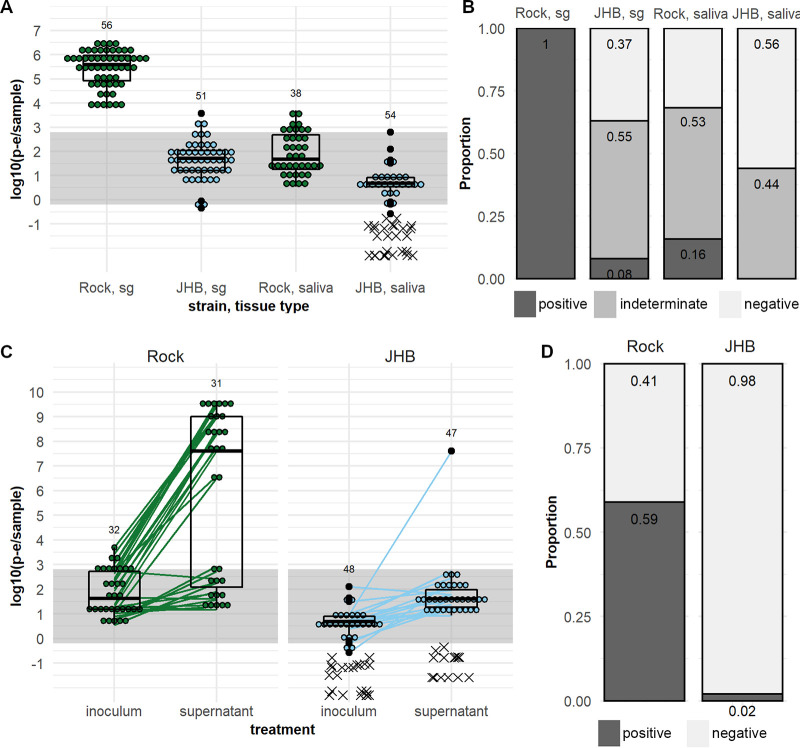
FIG 5.
Salivary gland and saliva transmission of pre-epidemic ZIKV by A. aegypti and C. quinquefasciatus after exposure by intrathoracic injection. ZIKV-Cambodia prevalence (A) and titers (B) in the salivary glands, and saliva of A. aegypti Rock strain and C. quinquefasciatus JHB strain at 7 dpi. (C) ZIKV-Cambodia titers in the inoculated saliva from A. aegypti Rock strain and C. quinquefasciatus HAI and JHB strains at 14 dpi and in the C6/36 cell supernatant at 6 days post-inoculation. (D) Prevalence of infectious (positive, dark gray) and non-infectious (negative, light gray) saliva samples by strain based on positive ZIKV outcomes in the C6/36 cell supernatant. Titers are displayed as log10 (p-e/sample), with individual samples with detectable qRT-PCR product displayed as ● symbols and boxplots showing medians, interquartile ranges, and outliers by species; connecting lines indicate pre- and post-C6/36 RNA titers in paired samples. Samples without detectable qRT-PCR product are displayed as an x and were excluded from summary statistics. Samples falling within the gray bands are of indeterminate infection status; samples above the band are considered positive, and samples below the band are considered negative. Numbers above the data indicate total mosquitoes analyzed. Results are from N = 2 independent biological replicates.