Fig. 4. Hippocampal lesions did not impair SC.
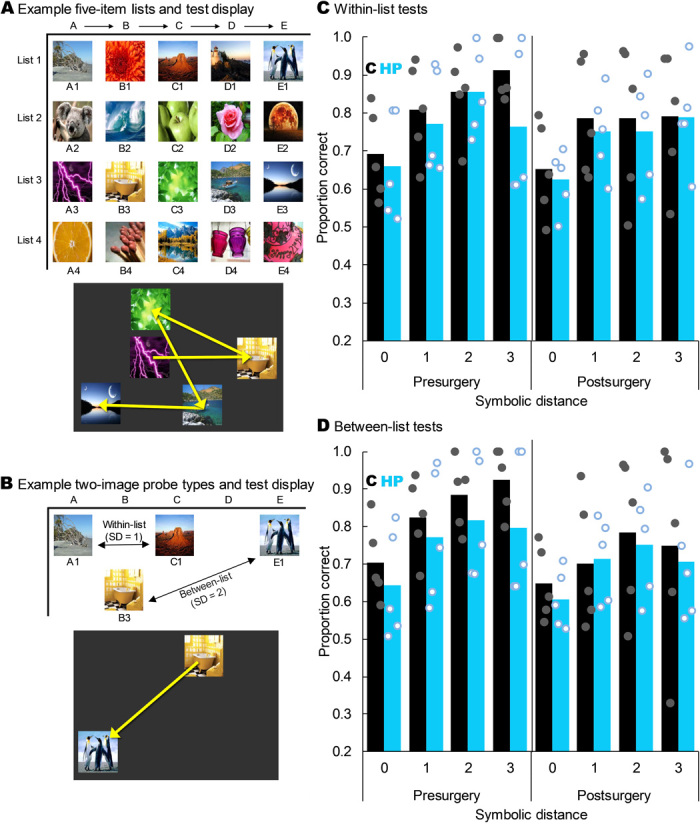
(A) Four example five-item lists and how one list might appear on the screen at test. The yellow arrows indicate the order in which the monkeys had to touch the images to earn food; these arrows were not shown to the monkeys. (B) Example two-image probe tests showing a within-list test at an SD of 1 and a between-list test at an SD of 2. The yellow arrow on the example screen shows the order in which the monkeys had to touch the images to earn food and was not visible during test. (C) Proportion correct on within-list probe tests as a function of SD, group, and experimental time point. Monkeys with hippocampal damage did not perform less accurately than controls overall (t8 = −0.833, P = 0.429) or at any individual SD (all t8 < 0.54, all P > 0.603). All monkeys showed a robust SDE (F3,24 = 25.303, P < 0.001), but there was no main effect of lesion group or interaction of group with any factor (all P > 0.05). Bars represent group means, and dots represent individual monkeys jittered along the x axis to help visualize individual performance. (D) As in (C) but for between-list tests. All monkeys showed a robust SDE (F1.549,12.390 = 19.626, P < 0.001), but there was no main effect of group or interaction of group with any factor (all P > 0.05). Stimuli images from Flickr under a Creative Commons CC BY 2.0 Generic License.
