Fig. 3. Response behaviors of the potentiometric mechanotransducers.
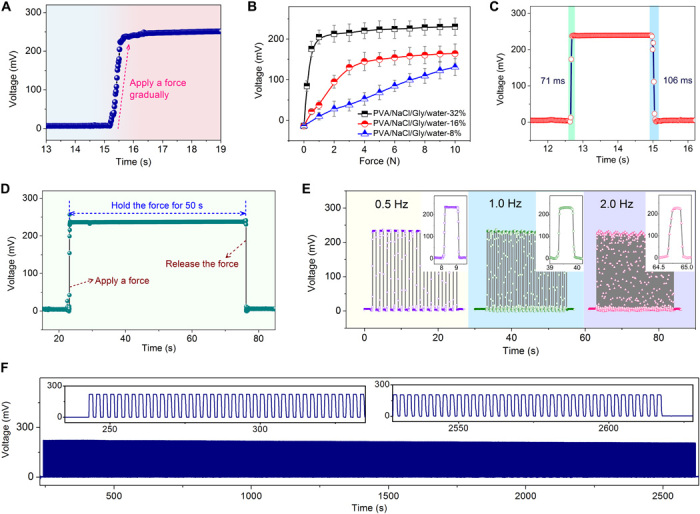
(A) Recorded voltage signal of a mechanotransducer while gradually applying a force on the device, showing a continuous and smooth mechanotransduction behavior. (B) Response behaviors of mechanotransducers with ionic composites of different Gly content. PVA/NaCl/Gly/water-X% signifies that the weight ratio of Gly:PVA is X%. Gly enables efficient regulation of the electrical impedance and the softness of the ionic composites and thus can tune the sensing behavior of the mechanotransducers. Ionic composite of PVA/NaCl/Gly/water-32% is used to fabricate mechanotransducers unless otherwise specified. (C) Response and recovery behaviors of the mechanotransducer. (D) Recorded voltage signal of the mechanotransducer while applying a static force on the device for 50 s. The voltage signal under the static force is nearly constant, verifying the ability of the mechanotransducer to record static mechanical stimuli. (E) Voltage signal variation of the mechanotransducer when applying a dynamic force (0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 Hz, respectively) on the device, indicating the capability to monitor low-frequency dynamic stimuli. (F) Reliability test of the mechanotransducer by loading and unloading a force on the device for 1000 cycles.
