Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the design of an integrated nanozyme with cascade anti-ROS activity for IBD therapy.
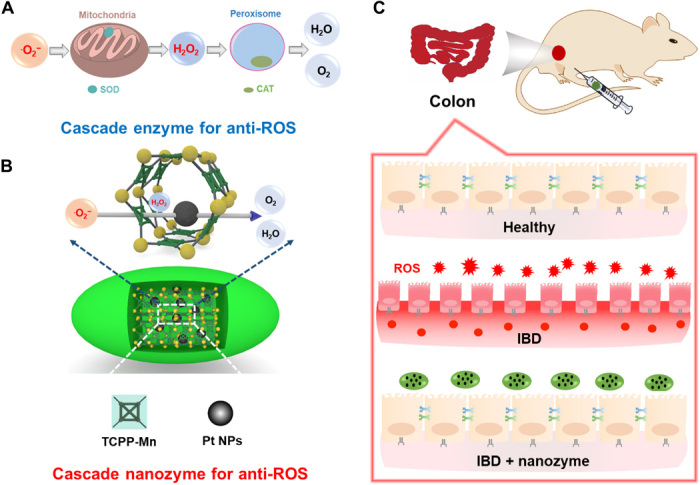
(A) Cellular cascade enzymes for anti-ROS. The therapeutic efficacy of such a system is limited because of the different subcellular locations of SOD and CAT enzymes and limited extracellular stability. (B) Constructing a cascade nanozyme for anti-ROS therapy by embedding Pt NPs inside PCN222-Mn MOF. Nanoscale proximity of catalytic active sites promotes the cascade reactions. (C) The IBD of mice can be effectively relieved through treatment with the integrated cascade nanozyme.
