Figure 3.
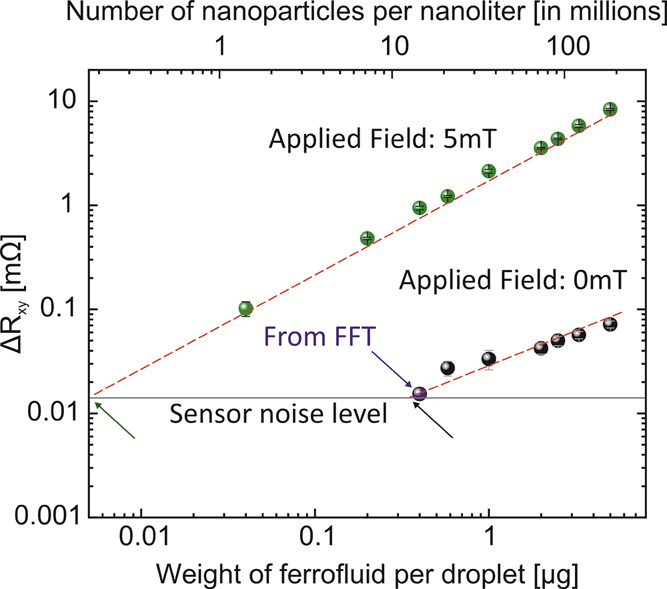
Sensor response while measuring 100 nL droplets containing ferrofluid at different concentrations when the droplets are biased in the geomagnetic field (black points) and biased to 5 mT using Helmholtz coils (green points). In the geomagnetic field, relying on the analysis of the signal in time domain, the limit of detection corresponds to 0.58 μg of nanoparticles per droplet. Fourier transformation of the time-dependent signal allowed detection of droplets containing an even lower concentration of nanoparticles down to 0.4 μg (blue arrow and Figure S6). Utilizing a field of 5 mT using Helmholtz coils, the detection limit is improved by an order of magnitude. Droplets containing 40 ng of magnetic nanoparticles per droplet can be readily detected. The extrapolated theoretical detection limit is located at 0.25 μg in the geomagnetic field (black arrow) and 5 ng in the 5 mT magnetic field (green arrow). The red dashed lines are guides for the eye, and each shown data point is an average of over 50 droplets.
