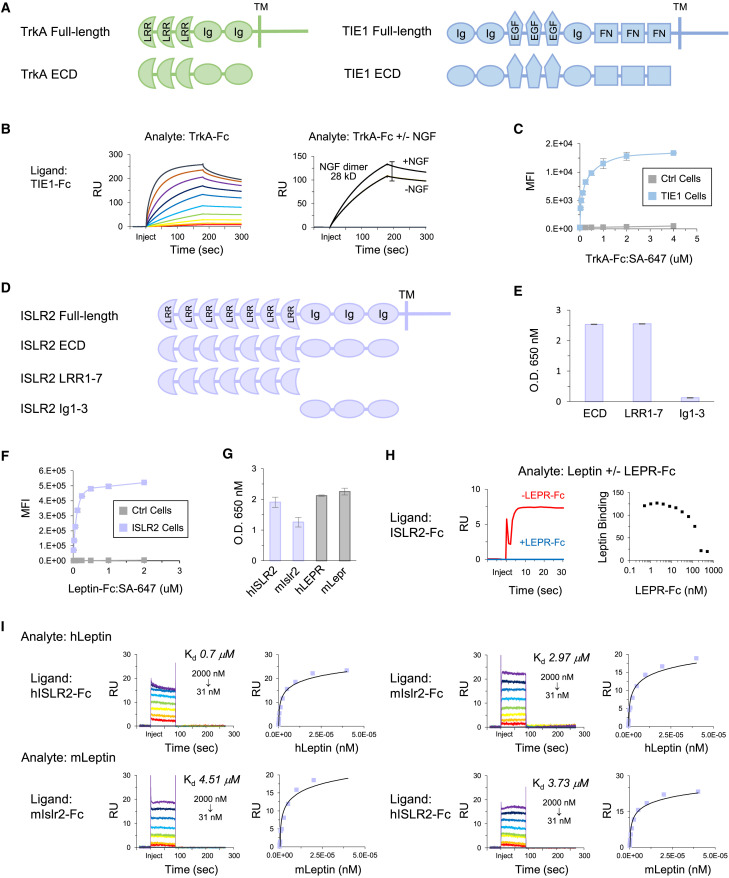
Figure 6.
TrkA Interacts with TIE1 and Leptin Interacts with ISLR2
(A) Protein domain structures of TrkA and TIE1.
(B) Left: SPR sensorgram for TrkA analyte (2-fold dilutions; 2–2,048 nM) binding to TIE ligand. Right: SPR sensorgram for 100 nM TrkA analyte ± 128 nM NGF binding to TIE1 ligand.
(C) Cell staining of full-length TIE1-transfected and control cells with TrkA-Fc:SA-647 and analysis by flow cytometry. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(D) Protein domain structures of ISLR2 ECD and truncations.
(E) ECIA of leptin-5AP with ISLR2 ECD-Fc, LRR1-7-Fc, and Ig1-3-Fc. Background subtracted data are represented as mean ± SD.
(F) Cell staining of full-length ISLR2-transfected and control cells with leptin-Fc:SA-647 and analysis by flow cytometry. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(G) ECIA of human leptin-5AP with human ISLR2-Fc and mouse Islr2-Fc. LEPR-Fc and Lepr-Fc; positive controls. Background subtracted data are represented as mean ± SD.
(H) Left: SPR sensorgram for 128 nM leptin ± 256 nM LEPR analyte binding to ISLR2 ligand. Right: SPR data showing 128 nM leptin analyte binding to ISLR2 ligand following pre-incubation with increasing concentrations of LEPR (2-fold dilutions; 0.5–512 nM).
(I) SPR sensorgrams and steady-state curves for monomer human and mouse leptin analytes (2-fold dilutions; 31–2,000 nM) binding to human ISLR2 and mouse Islr2 ligands.
RU, resonance units; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; Ig, immunoglobulin-like domain; FN, fibronectin type III domain; LRR, leucine-rich repeat; EGF, epidermal growth factor repeat domain; TM, transmembrane; Ctrl, control.
See also Figures S5 and S7 and Data S5.