Table 4.
Results of reference runs (four runs with four Metropolis-coupled chains each) and test runs (16 single-chain runs) for each of the six data sets
| R.20M | R.10M | 2 eSPR : 1 eTBR | 2 pSPR1 : 1 pTBR1 | 2 pSPR2 : 1 pTBR2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data set | ASDSF | ASDSF |
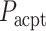
|
ASDSF |
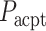
|
ASDSF |
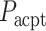
|
||||
| SQ10 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.097 | 4.56%, 3.78% | 0.037 | 8.52%, 12.1% | 0.012 | 8.63%, 12.2% | |||
| DA10 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.019 | 8.24%, 5.02% | 0.016 | 8.11%, 7.04% | 0.009 | 8.62%, 8.02% | |||
| LZ12 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 54.3%, 43.5% | 0.006 | 48.2%, 43.1% | 0.005 | 53.1%, 48.4% | |||
| CL12 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 18.0%, 12.7% | 0.006 | 18.6%, 16.9% | 0.006 | 19.8%, 18.8% | |||
| AZ12 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.031 | 4.88%, 4.18% | 0.009 | 6.60%, 8.70% | 0.017 | 7.14%, 10.0% | |||
| NP11 | 0.020 | 0.041 | 0.108 | 58.4%, 49.5% | 0.039 | 46.9%, 44.1% | 0.038 | 52.3%, 49.1% | |||
Notes: We first give the average standard deviation of split frequencies (ASDSF) for the reference runs after 20 and 10 million generations (R.20M and R.10M, respectively). Then we give the ASDSF values and average acceptance proportion (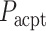 ) for 16 test runs using three different combinations of tree proposals. The reference tree samples after 20 million generations had ASDSF
) for 16 test runs using three different combinations of tree proposals. The reference tree samples after 20 million generations had ASDSF 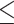 0.02 and were considered as ground truth in the detailed studies of the convergence and mixing behavior of tree proposals.
0.02 and were considered as ground truth in the detailed studies of the convergence and mixing behavior of tree proposals.
