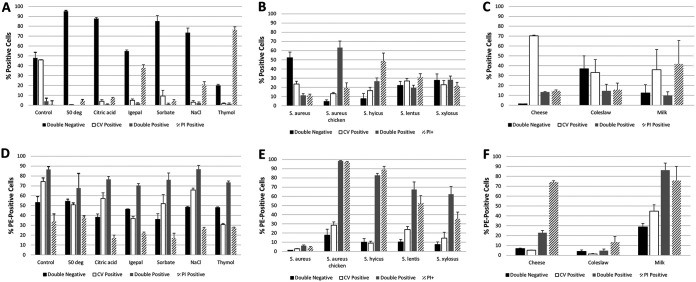
FIG 4.
(A) Mean percentages of cells of S. aureus chicken ready-meal isolate falling into one of four physiological groups (double negative, calcein violet positive only, double positive, and PI positive only) based on calcein violet (CV) and PI fluorescence after treatment with 0.09% (wt/vol) potassium sorbate, 12% NaCl, 0.09% sodium citrate, 0.5 % IGEPAL CO-630, or 0.25% (wt/vol) thymol or after heat treatment at 50°C for 30 min and analyzed using FCM (n = 3; χ2 = 436.45846, df = 18, P < 0.00001), as well as the binding of anti-human CD44 antibody by cells from these groups (D; n = 3; χ2 = 29.53591, df = 18, P = 0.04221). (B) Percentages of cells as analyzed using FCM of various Staphylococcus species falling into one of four physiological groups after incubation on stainless-steel surfaces for 24 h at 37°C (n = 5; χ2 = 154.15338, df = 12, P < 0.00001) and binding of anti-human CD44 antibody by cells from these groups (E; n = 5; χ2 = 21.05560, df = 12, P = 0.04957). (C) Percentages of cells as analyzed using FCM of S. aureus chicken ready-meal isolate spiked into cheese (n = 2), coleslaw (n = 3), or milk (n = 3) falling into one of four physiological groups based on calcein violet (CV) and PI fluorescence (χ2 = 77.37324, df = 6, P < 0.00001), as well as the binding of anti-human CD44 antibody by cells from these groups (F; χ2 = 44.72049, df = 6, P < 0.00001). In all cases, error bars indicate the standard errors of the mean.