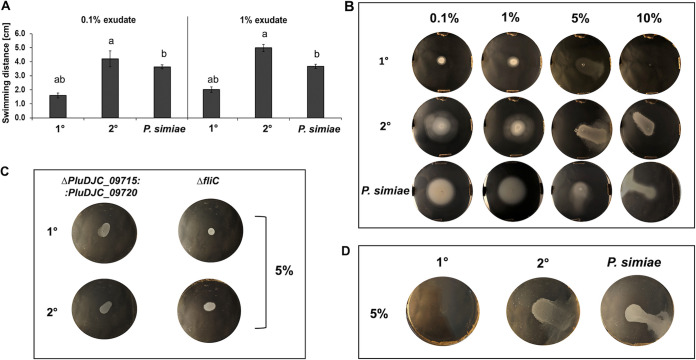
FIG 4.
Chemotaxis, swimming, and swarming. The chemotaxis assays were performed in LB swimming agar plates using the MetOH-extracted fraction of pea root exudates. (A) Quantification of the swimming assays shown in panel B using 0.1% and 1% pea plant root exudates. The plots show the swimming halo measured with ImageJ represented by the average and the standard deviation of four biological replicates (different lowercase letters between the bars indicate a P value of ≤0.05). (B) Chemotaxis assays of P. luminescens 1° and 2° cells as well as P. simiae WCS417 using 0.1%, 1%, 5%, and 10% of plant root exudates, respectively. P. luminescens 2° cells and P. simiae show swimming behavior at a concentration of 0.1% and 1% of plant root exudates, while at ≥5%, they showed swarming behavior. (C) Chemotaxis assays using P. luminescens 1° and 2° chemotaxis receptor ΔPluDJC_09715 ΔPluDJC_09720 (double deletion) and ΔfliC (negative control) mutants. (D) Swarming assays on M9 minimal medium with 5% of plant root exudates to exclude LB compounds to be responsible for swarming. All images represent one characteristic of four independently performed experiments with similar outcomes.