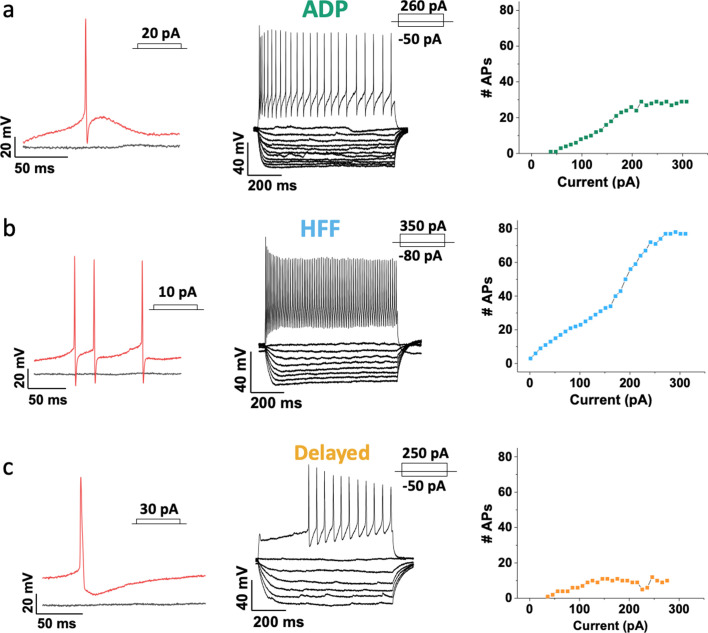
Figure 2. Three major Sst-expressing neuron subtypes in the VTA based on their firing properties.
From left to right: example traces of the action potentials (APs) (in red) evoked by rheobase current injection, black line represents the baseline with no current injected; example traces of subthreshold voltage-responses of the same cells to 800 ms current steps with 10 pA increment, together with voltage-responses to saturated excitation; cumulative spike counts after increasing currents steps. (a) ADP neurons showed salient afterdepolarization (ADP) at rheobase current and a visible adaptation in firing at the saturated level of excitation. (b) High-frequency firing neurons (HFF) displayed sharp prominent afterhyperpolarization at rheobase current and the highest number of APs at the saturated level of excitation. (c) Delayed neurons demonstrated a long delay preceding the firing at the saturated level of excitation. Slow afterhyperpolarization and low adaptation were distinctive features of this particular subtype.