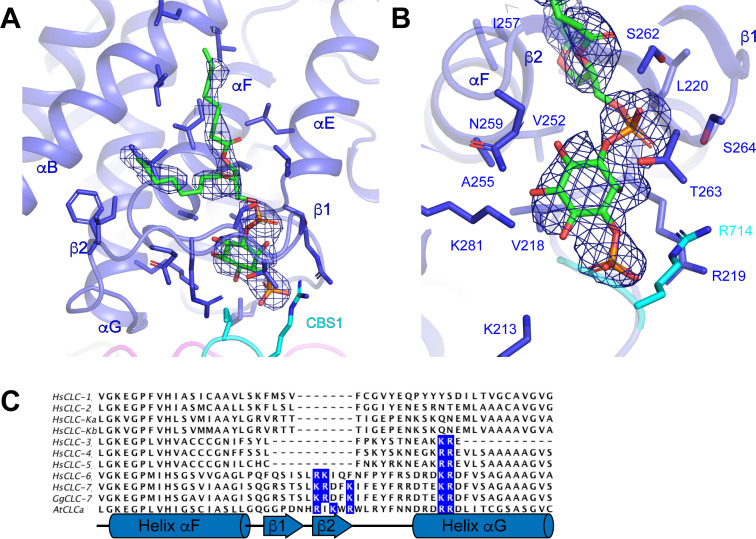
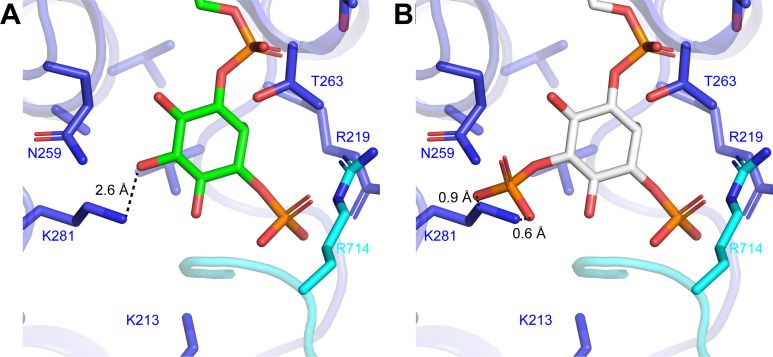
Figure 4. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate binding site.
(A) PI3P molecule shown as sticks. ggCLC-7 N-terminal domain is colored in magenta, transmembrane domain in blue, CBS1 in cyan and CBS2 in green with residues that interact with PI3P shown as sticks. Experimental cryo-EM density for PI3P is shown as blue mesh contoured at 10 σ threshold. (B) Coordination of the PI3P by ggCLC-7. Residues that interact with PI3P head group are shown as sticks. Experimental cryo-EM density for PI3P is shown as blue mesh contoured at 10 σ threshold. (C) Sequence alignment of helices αF and αG in ggCLC-7 with human CLC-1, CLC-2, CLC-Ka, CLC-Kb, CLC-3, CLC-4, CLC-5, CLC-6, CLC-7 and A. thaliana CLC-a. Positions of lipid coordinating Lys266, Arg267, Lys270, Lys281 and Arg282 in ggCLC-7 are highlighted in blue.