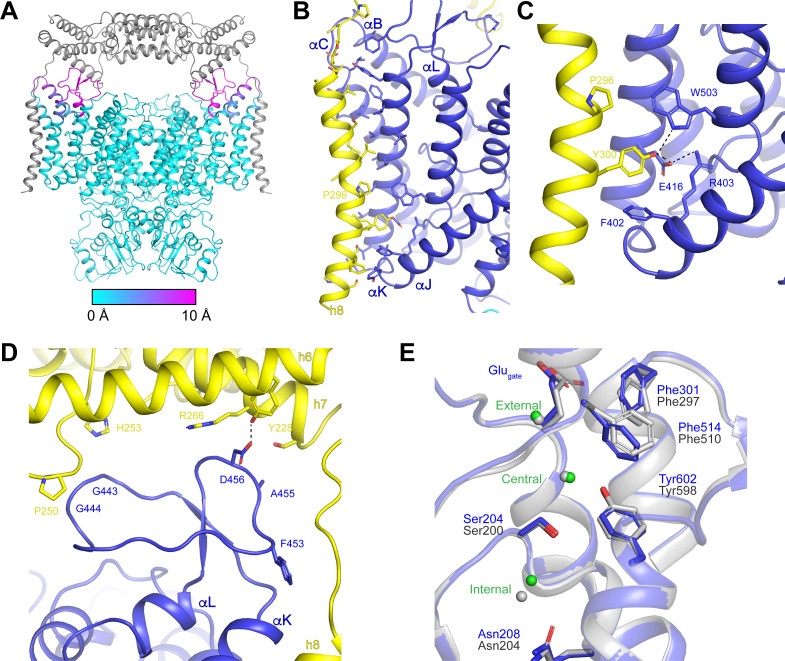
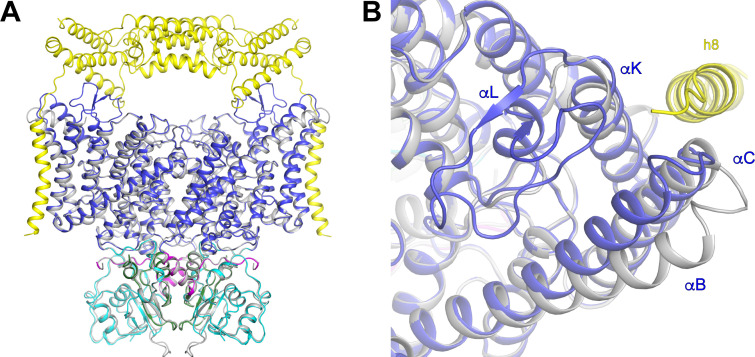
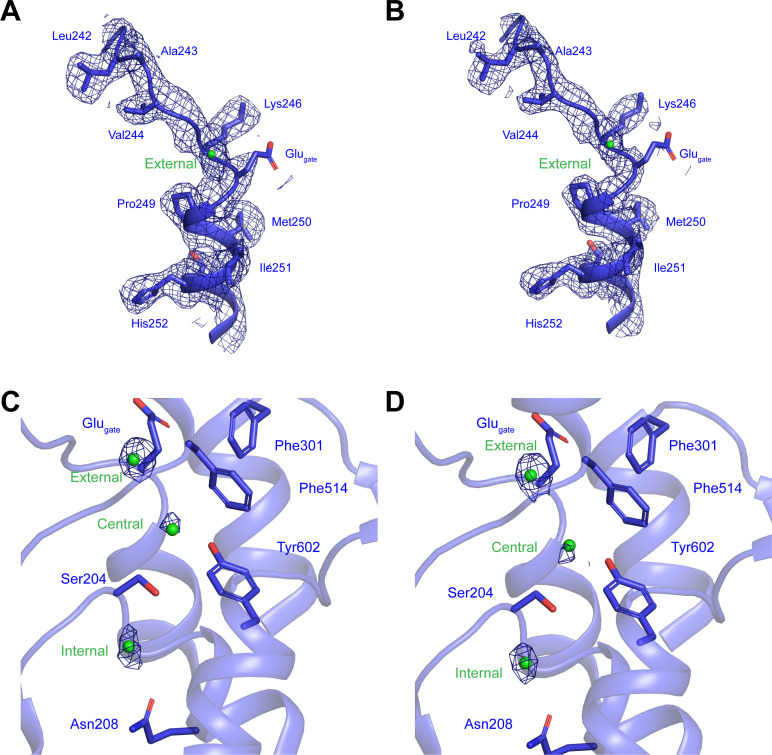
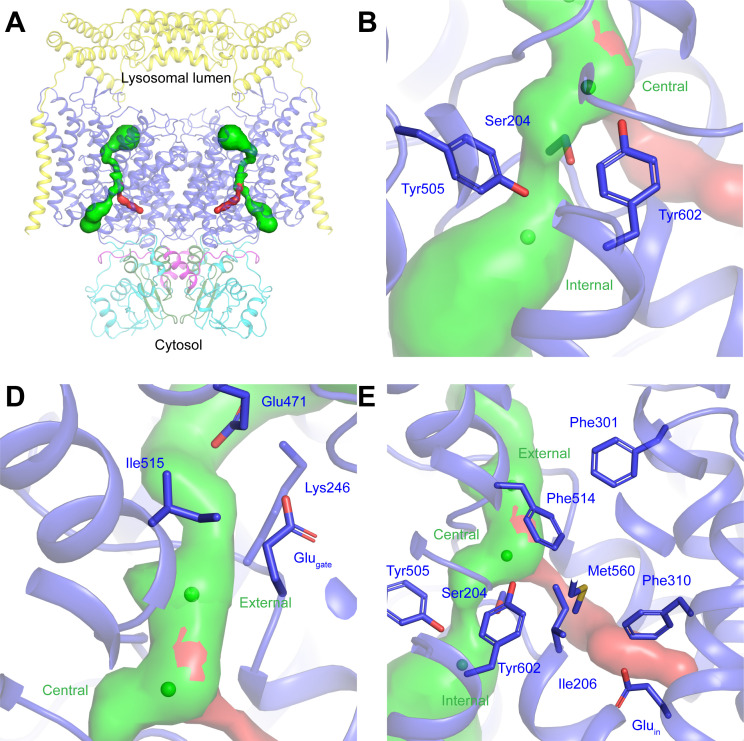
Figure 7. OSTM1-induced conformational changes.
(A) Structure of hsCLC-7/OSTM1 with CLC-7 colored by Cα displacement compared to ggCLC-7 and OSTM1 colored in grey. (B) hsCLC-7/OSTM1 transmembrane domain interface. Residues that participate in the interaction are shown as sticks. CLC-7 is colored in blue and OSTM1 is colored yellow. (C) Polar interaction network in the transmembrane domain interface between CLC-7 and OSTM1. (D) Loop between αK and αL is stabilized by interactions with OSTM1 luminal domain. (E) Cl--conduction pathways of human CLC-7/OSTM1 (colored by domain) and ggCLC-7 (grey). Interacting side chains are shown as sticks and Cl- ions are shown as spheres. Blue residue numbers correspond to human CLC-7 and grey numbers correspond to ggCLC-7.