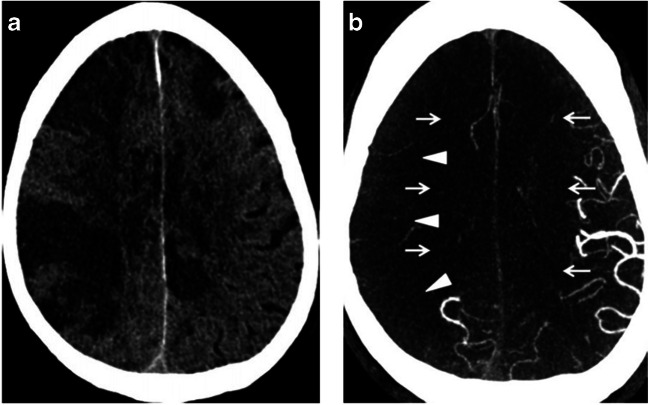
Fig. 1.
a NCCT of the head in a COVID-19 patient demonstrates findings of AIS, including hypoattenuation of the brain parenchyma, loss of gray-white differentiation, and sulcal effacement. b Axial CTA of the head in the same patient demonstrates reduced vascular filling in branches of the right middle cerebral artery (arrowheads) and bilateral anterior cerebral arteries (arrows). Reference: Goldberg MF, Goldberg MF, Cerejo R, Tayal A. Cerebrovascular Disease in COVID-19. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2020. doi:10.3174/ajnr.a6588. (Permission granted)