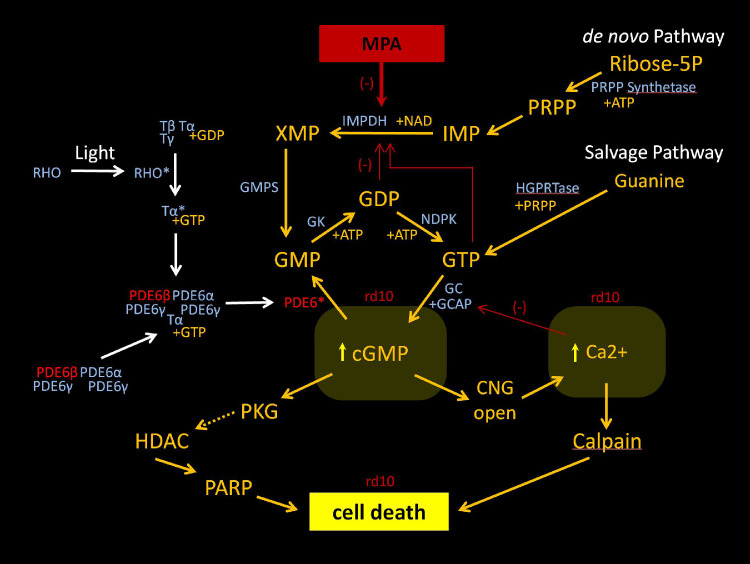
Figure 9.
Mechanism of action of MPA. This schematic shows the guanine nucleotide synthesis via the de novo and salvage pathway, and the mechanism of action of MPA inhibition of the de novo pathway. The phototransduction cascade is also shown, highlighting the mutant PDE6b subunit and PDE6 enzyme. In rd10 mice, the mutation leads to intracellular elevation of cGMP and calcium, triggering cell death via an alternative pathway or calpain, respectively. The alternative pathway is associated with PKG, HDAC, and PARP.4 PRPP, phoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate; HGPRTase, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; IMP, inosine 5′-monophosphate; XMP, xanthosine monophosphate; GMPS, GMP synthetase; RDR, ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase; GK, guanylate kinase; NDPK, nucleoside diphosphate kinase; GC, guanylate cyclase; GCAP, GC-activating protein; PKG, protein kinase G; HDAC, histone deacetylase; PARP, poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase; CNG, cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; RHO, rhodopsin; T, transducin; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; *activate form of molecule.