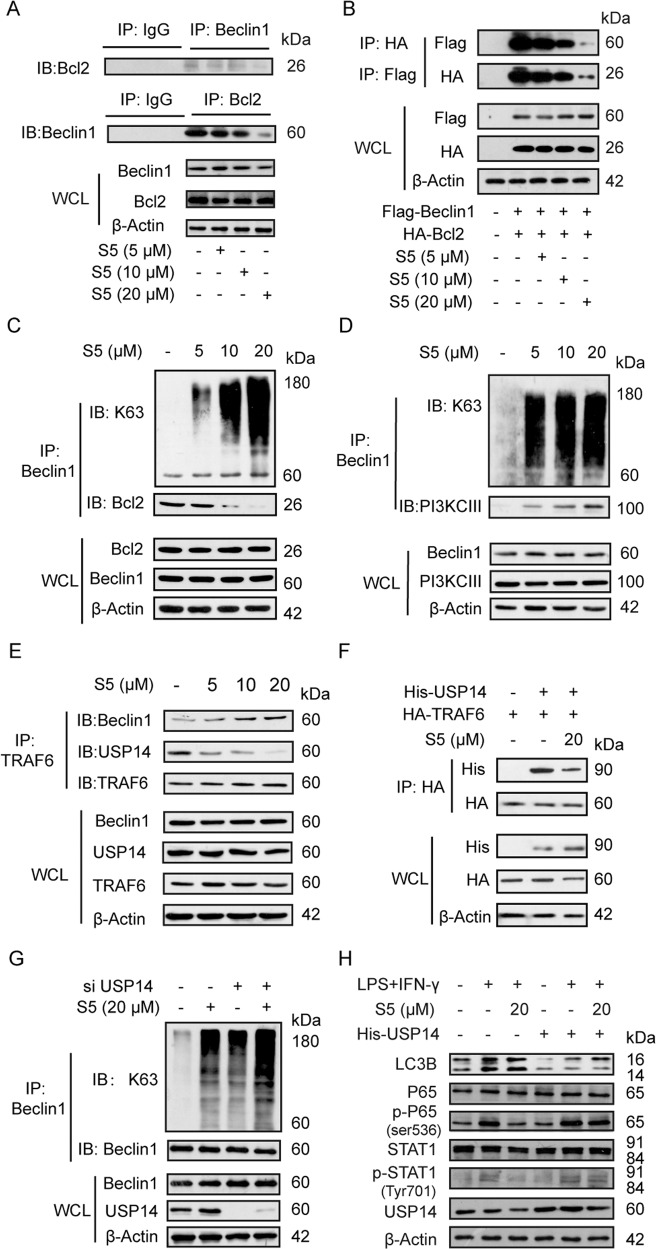
Fig. 6. S5 increases Beclin1 ubiquitination and disturbs Beclin1–Bcl2 interaction.
a RAW264.7 cells were incubated with various dosages of S5 (5, 10, and 20 μM) for 6 h. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to analyze Beclin1–Bcl2 interaction. b HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-Beclin1 and HA-Bcl2 plasmids for 48 h, and incubated with various dosages of S5 for 6 h. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to analyze the interaction of Flag-Beclin1 and HA-Bcl2. c, d RAW264.7 cells were incubated with various dosages of S5 for 6 h. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments analyzed K63-ubiquitination of Beclin1 and the interaction of Beclin1 with bcl-2 or PI3KCIII. e RAW264.7 cells were incubated with various dosages of S5 for 6 h. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments analyzed the interaction of TRAF6 with USP14 or Beclin1. f HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-TRAF6 and His-USP14 for 48 h, and incubated with S5 (20 μM) for 6 h. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to analyze the interaction of HA-TRAF6 and His-USP14. g RAW264.7 cells were transfected with siRNA of USP14 or si-Control for 48 h, and co-immunoprecipitation was used to analyzed K63-ubiqutination of Beclin1 with or without S5 treatment. h RAW264.7 cells were transfected with His-USP14 plasmid for 48 h. P62, LC3B, p-P65, P65, p-STAT1, and STAT1 expression were detected by western blot. The relative statistics of h was shown in Supplementary Fig. S4. Data are means ± SEM of five independent experiments. ns nonsignificant, *P < 0.05 vs. LPS and IFN-γ group.