Figure 4. T. gondii inhibits nuclear translocation of IRF-7 in response to HSV-1 without affecting phosphorylation of IRF-7.
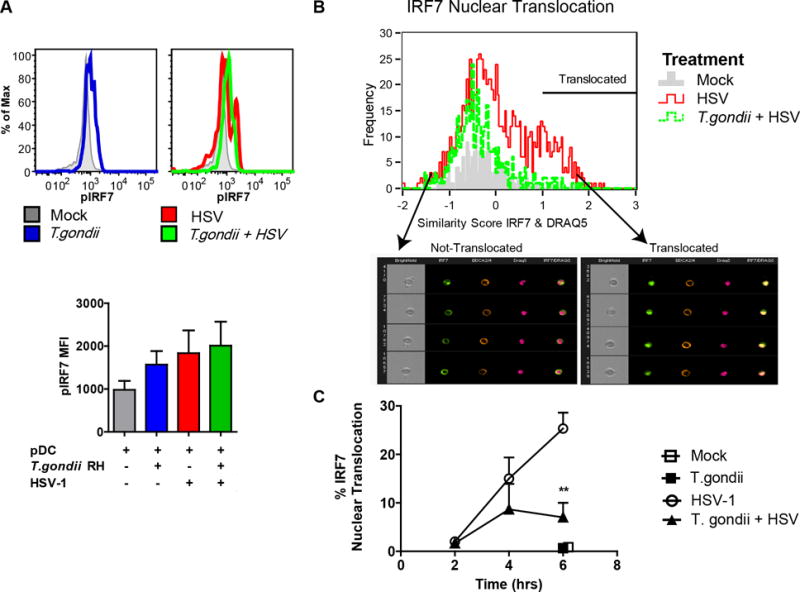
A, PBMC were pre-infected with T. gondii at an MOI of 4, followed by stimulation with HSV, MOI 1. 3hrs after stimulation with virus, fixed pDC were stained using anti-HLA-DR and CD123; following ethanol permeabilization intracellular phosphorylation of IRF7 was assessed using pIRF7-PE (pS477/pS479) and measured using flow cytometry. Representative flow plots from a single experiment are shown in the top panel, and summary data are shown in the lower panel for 3 independent experiments. B, Enriched pDC were pre-infected with T. gondii as described above and exposed to HSV-1 for 2, 4 and 6 hrs; BDCA2 and BDCA4 positive pDC were then analyzed for cytoplasmic and nuclear distribution of IRF7 using ImageStream and Amnis IDEAS software. Representative data are shown from the 4-hr timepoint. IRF7 nuclear translocation in pDC was determined by first creating an object mask for nuclear stain (DRAQ5), and then analyzed using built in function of similarity between IRF7 and nuclear mask. A histogram overlay was generated for comparison of IRF7 nuclear translocation in Mock (gray), HSV-1 (red), and in T. gondii pre-infected and HSV-1 treated pDC (green) pDC. Arrows indicate bin with representative images of not-translocated (left) and translocated (right) events. C, Kinetics of IRF7 nuclear translocation and the effect of T. gondii infection on IRF7 translocation in B were analyzed for statistical significance (n=3).
