Fig. 3.
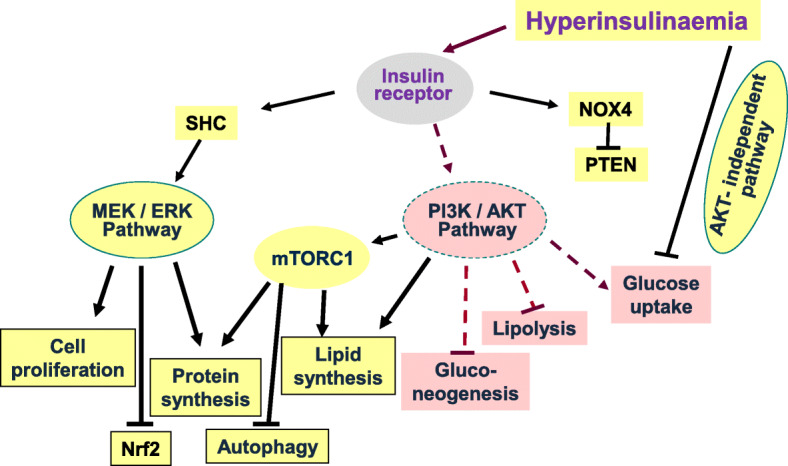
Signaling of insulin during insulin resistance. During insulin resistance, signaling through AKT kinases is partially impaired. Not all AKT-dependent pathways are affected, as well as other signaling pathways, indicating that insulin resistance is selective. Therefore, hyperinsulinemia, in the presence of insulin resistance, promotes anabolic cell activities via the MEK–ERK pathway and via mTORC1. Although the PI3K/AKT pathway is impaired during insulin resistance, and provides only insufficient translocation of GLUT4 for glucose uptake and deficient activation of eNOS, there appears to be a normal activation of mTORC1. In addition to the anabolic consequences of signaling via the MEK/ERK pathway depicted in the figure, there is enhanced expression of ET-1 and PAI-1 (not shown), as well as inhibition of autophagy and of the nuclear factor Nrf2, which compromises cell constituent turnover and cell defense mechanisms to radical stress, respectively. Hyperinsulinemia downregulates glucose uptake not only via dampening the PI3K/AKT pathway (“insulin resistance”) but also via as yet unknown other pathways
