Figure 2.
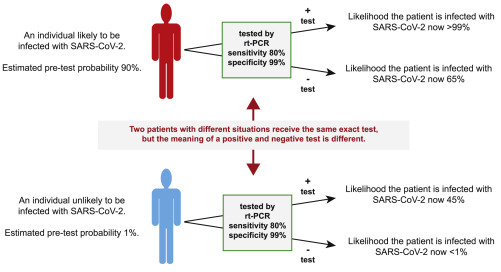
Test Result Interpretation Is Largely Affected by Whether Other Factors Suggest the Tested Individual Is Infected with SARS-CoV-2
If the same exact RT-PCR test is given to 2 different individuals—one whose presentation is consistent with SARS-CoV-2 infection and one whose presentation is not—then the probability that a positive test indicates an infection with SARS-CoV-2 can vary greatly. For example, the individual whose presentation suggests a 90% chance of infection is >99% likely to have an infection if he or she tests positive and 65% likely to have an infection if he or she tests negative. The individual at low risk remains more likely not to have an infection if he or she tests positive, and the absolute reduction in the chance that he or she has a SARS-CoV-2 infection has reduced by <1%.
