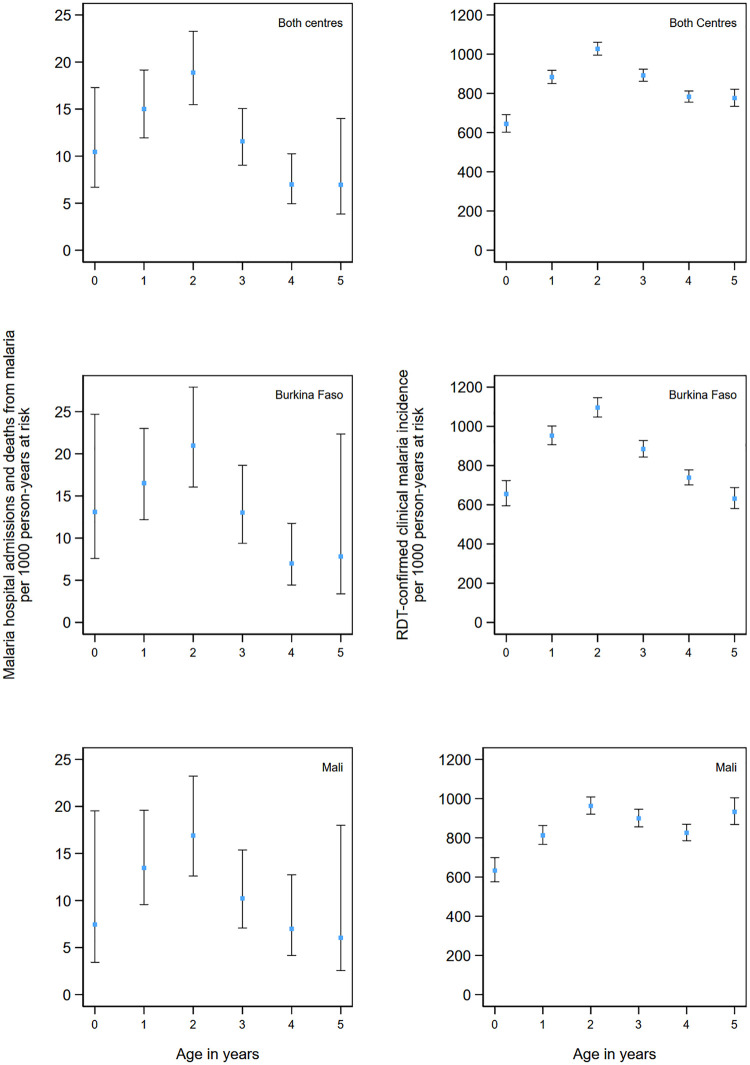
Fig 1. Incidence of malaria hospital admissions and deaths from malaria and clinical malaria by age.
Incidence of malaria hospitalisations and deaths from malaria (left panel) and uncomplicated clinical malaria (right panel) by age group over the study period. Malaria hospitalisations and deaths from malaria were defined as hospital admission with a diagnosis of malaria and blood-slide–or RDT-confirmed P. falciparum infection or deaths for which malaria was listed as the primary diagnosis. Clinical malaria was defined as attendance at study health facility with a history of fever or measured temperature ≥37.5 °C, with malaria infection confirmed by RDT. Incidence rates are presented per 1,000 person-years and include repeat events in the same child, provided the healthcare contact occurred more than 7 days apart. Vertical bars show 95% CIs. CI, confidence interval; RDT, rapid diagnostic test.