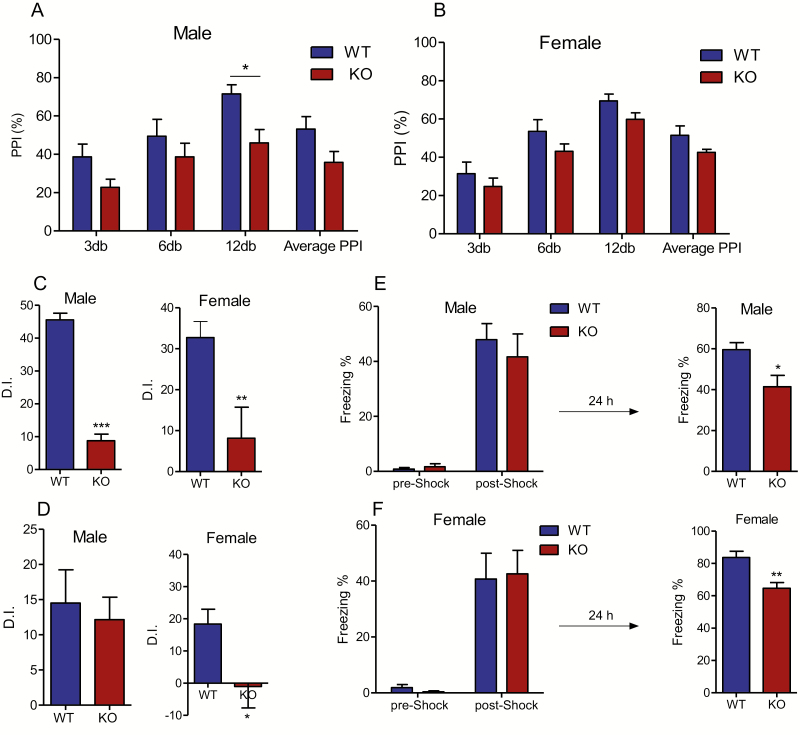
Figure 4.
Effect of MCHR1 germline ablation on prepulse inhibition and different types of memory. (A) Prepulse inhibition ratio in male: 2-way ANOVA, genotype effect (F1,48 = 14.55, P = .0004), prepulse intensity effect (F3,48 = 6.27, P = .001) and genotype x prepulse intensity (F3,48 = 0.447, P = .72) followed by Bonferroni post hoc test: WT vs KO, *P < .05 (n = 7). (B) Prepulse inhibition ratio in female, 2-way ANOVA, genotype effect (F1,56 = 6.8, P = .006), prepulse intensity effect (F3,56 = 20.66, P < .0001), and genotype × prepulse intensity (F3,56 = 0.067, P = .98) followed by Bonferroni post hoc test: wild type vs KO, P > .05 (n = 8). (C) Discrimination index in the NOR assay: male: t = 12.83, P = .0001. Unpaired student t test: wild type vs MCHR1 KO, *** P < .001 (n = 7 and 6 for wild type and MCHR1 KO, respectively), female: t = 3.02, P = .007. Unpaired student t test: wild type vs MCHR1 KO, *** P < .001 (n = 12 and 10 for wild type and MCHR1 KO, respectively). (D) Discrimination index in the location-dependent object recognition assay: male: t = 0.28, P = .178, Unpaired student t test: WT vs MCHR1 KO (n = 8), female: t = 2.65, P = .0.015; Unpaired student t test: wild type vs MCHR1 KO, *P < .05 (n = 12). (E) Male: Percentage of the freezing behavior in contextual fear conditioning assay (n = 8). Training/Conditioning: 2-way ANOVA, genotype effect (F1,28 = 0.2789, P = .6), stage effect (F1,28 = 72.20, P < .0001), test: unpaired t test (t = 2.8, P = .012), WT vs KO: *P < .05. (F) Female: Percentage of the freezing behavior in contextual fear conditioning assay (n = 9). Training/Conditioning: 2-way ANOVA, genotype effect (F1,32 = 0.0009, P = .97), stage effect (F1,32 = 41.79, P < .0001), Test: Unpaired t test (t = 3.6, P = .002), **P < .01.