FIGURE 1.
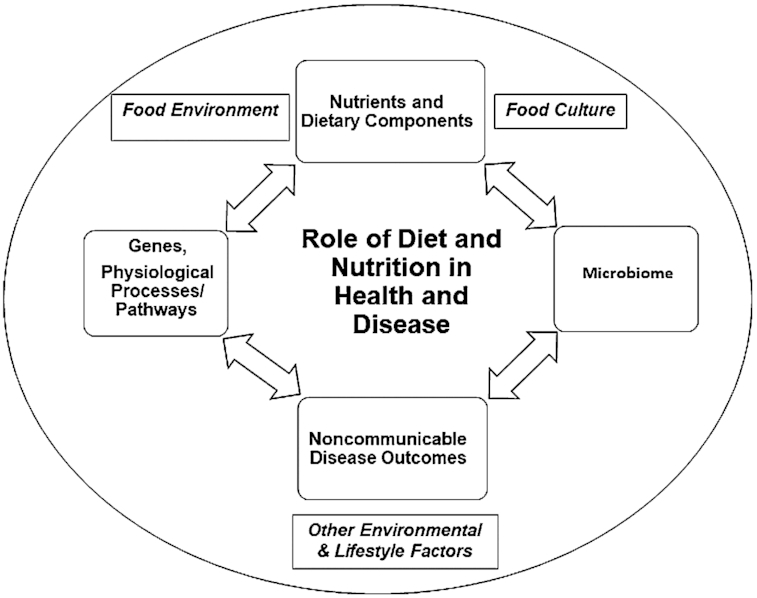
Bidirectional interaction between dietary components and physiologic systems embedded in food consumption driven by food environments and further influenced by cultural and lifestyle factors. Consumption of nutrients such as fatty acids, amino acids, vitamins, trace elements, and bioactive compounds has an impact on host physiology, affecting both the health status and susceptibility to disease. Metabolism of dietary components is also influenced by the genetic make of an individual. In addition, dietary components may directly affect gut microbiota composition and function, which may exacerbate metabolic and physiologic outcomes, further influencing disease susceptibility. Host physiology and altered susceptibility to disease in turn affect how these dietary substances are metabolized.
