Fig. 1. Schematic illustrations of the laser writing process and its applications.
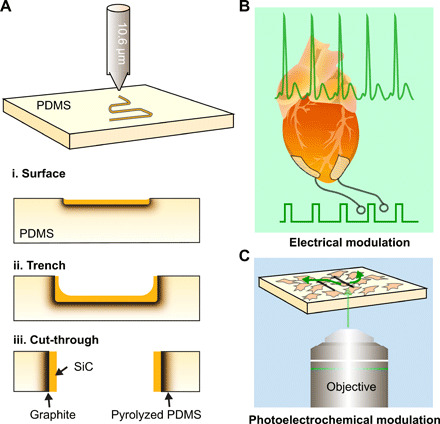
(A) CO2 laser writing a pattern on a PDMS substrate wherein the pattern can be (i) on the surface, (ii) a trench, or (iii) a cut-through leading to the formation of two distinct pieces. Architectures (i) to (iii) arise as a function of the laser power and writing speed. A graphite layer forms beneath the SiC because of the nature of the ablation process. (B) Laser-written electrodes are flexible electrodes that can integrate with a heart and stimulate it with electrical impulses leading to its pacing. (C) Laser-written circuits can be used for photoelectrochemical modulation of interconnected cellular ensembles.
