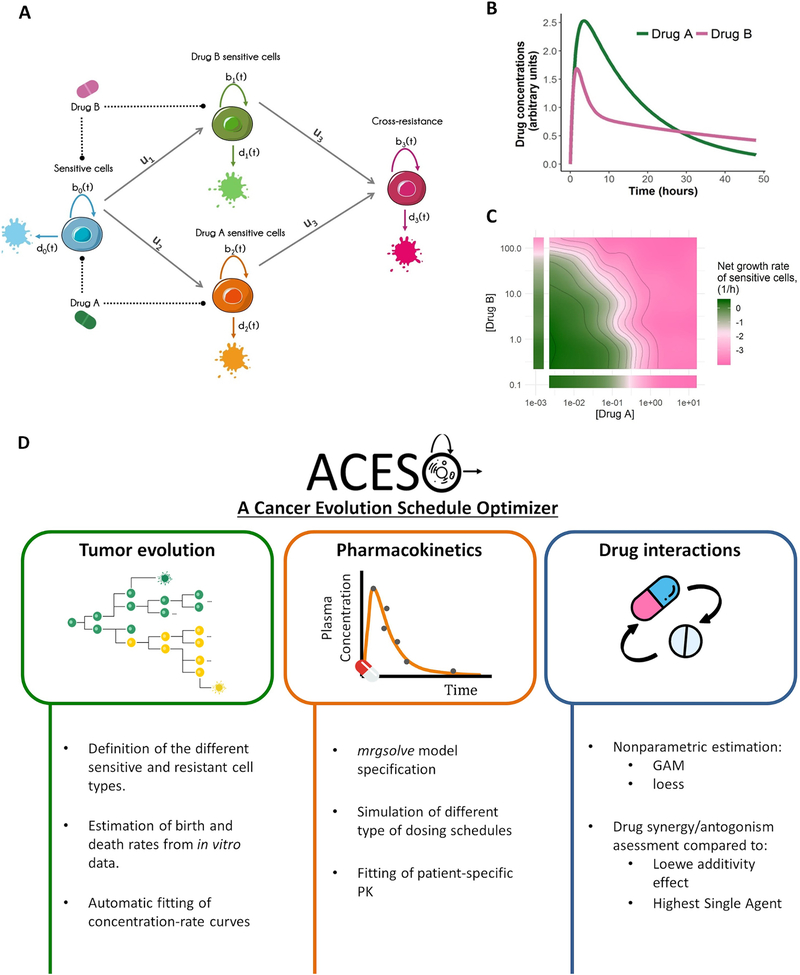
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of: A) a four-type branching process with cross-resistance. The type-0 cell (blue), which is sensitive to both drugs A and B, proliferates at rate b0(t), dies at rate d0(t) and can accumulate mutations at probability ui per cell division to give two different cell types, type-1 (green) and 2 (orange), which are sensitive to either drug A or drug B. Type-1 and 2 cells can mutate again and become resistant to both drug A and B (type 3 cells, magenta). Each resistant cell type has its own proliferation and death rates, bi(t) and di(t), with i = 1,2... B) Drug concentration-time profile governed by the pharmacokinetic parameters of drug A and B after a single-dose administration. C) Graphical evaluation of how the net growth rate of type-0 cells changes under the effects of different drug concentrations with a contour plot and isoboles (i.e. contour lines of equal drug effect). This representative example is based on the additive effect of the drugs in panel B with additional synergistic/antagonistic effects. D) Main functionalities of ACESO. PK refers to pharmacokinetics, GAM to Generalized Additive Models and loess to locally weighted scatterplot smoothing.