Figure 2:
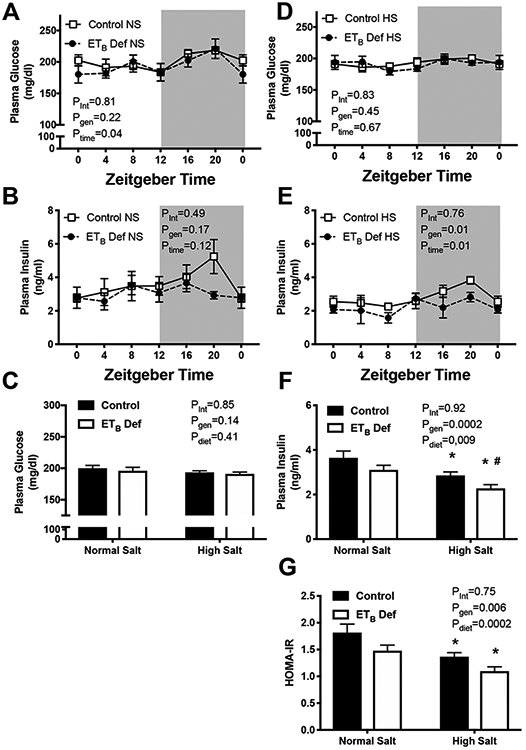
Chronic high salt (HS) intake reduces circulating insulin in endothelin B deficient (ETB def) rats. Transgenic control and ETB def rats were fed either normal salt (NS) or HS diet for 2 weeks, and tissues were collected in non-fasted animals under anesthesia in 4 hour intervals. A & D) plasma glucose (mg/dL; n=5-7/group), B & E) circulating insulin (ng/ml; n=5-7/group), C) average plasma glucose of all time points (n=36-40/group), and F) average plasma insulin concentration of all time points (n=36-40/group) and and G) HOMA-IR caculated from non-fasting insulin and glucose. *p<0.05 vs. NS control; # p<0.05 vs NS ETB def. ANOVA table Key: interaction (int), genotype (gen), time of day (time)
