Figure 5: AXL targeting overcomes resistance to radiation therapy.
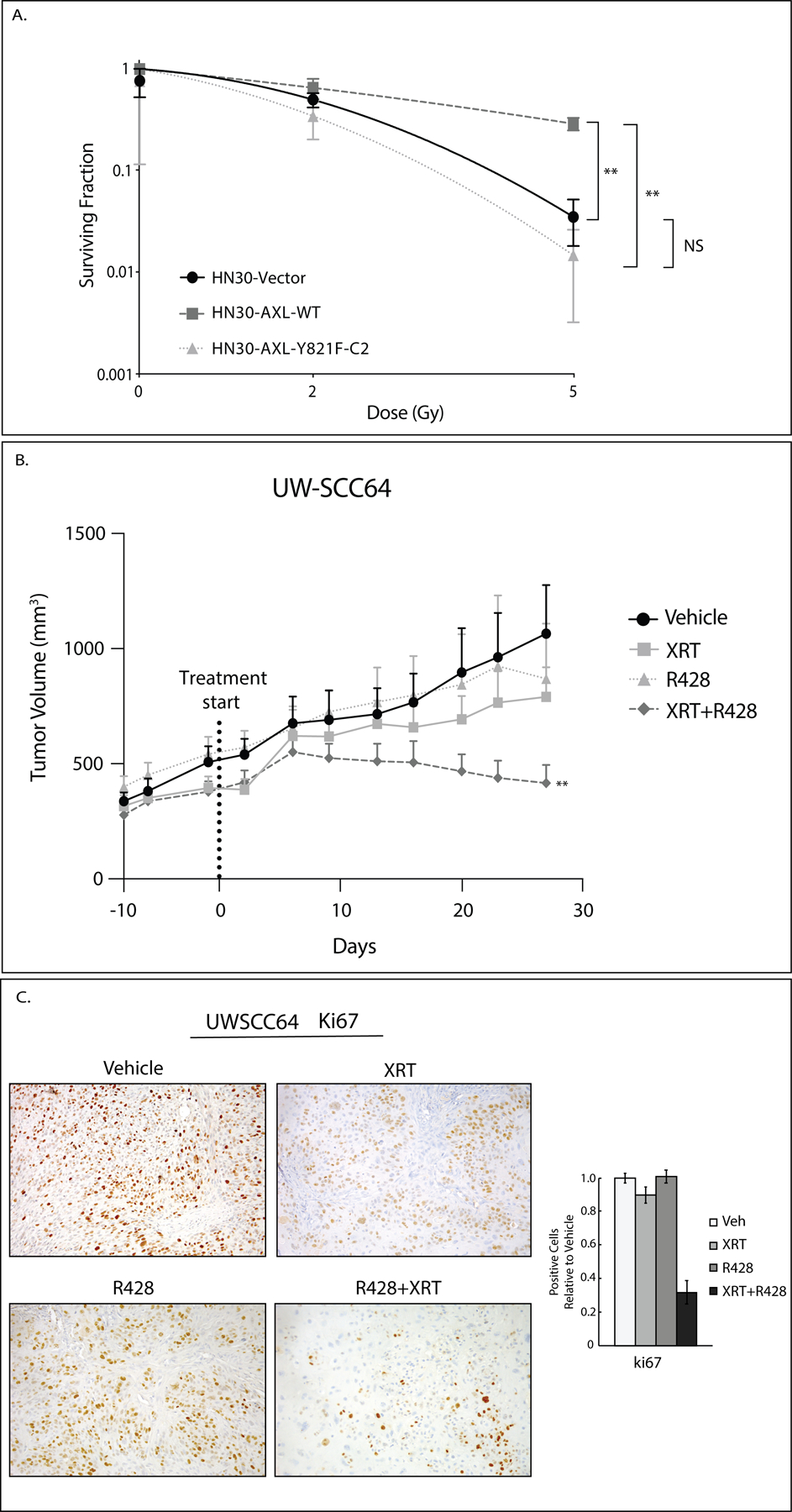
A: Radiosensitivity of HN30 cell lines (Vector, AXL-WT, AXL-Y821F-C2) was evaluated by clonogenic survival analysis. Cells were plated and 24 hours later treated with radiation (0Gy, 2Gy, 5Gy). Mean values, SEs, and statistical analyses were derived from replicates within the experiment. **, P<.01; NS, not significant.
B: PDX UW-SCC64 was implanted into flanks of nude mice and treated with vehicle (oral gavage, methylcellulose, twice daily) (n=13), XRT (3Gy twice weekly) (n=10), R428 (oral gavage, 25mg/kg, twice daily) (n=10), or combination of radiation with R428 (n=11) for 28 days. The vehicle and R428 arms are the same as shown in Figure 1B. Data was analyzed using linear mixed models where volume was modeled on natural-log scale. **, P<.01 for combination compared to single treatments.
C: Tumors from study shown in 5B were stained for Ki67 using IHC. Image quantification is shown.
