Fig. 3.
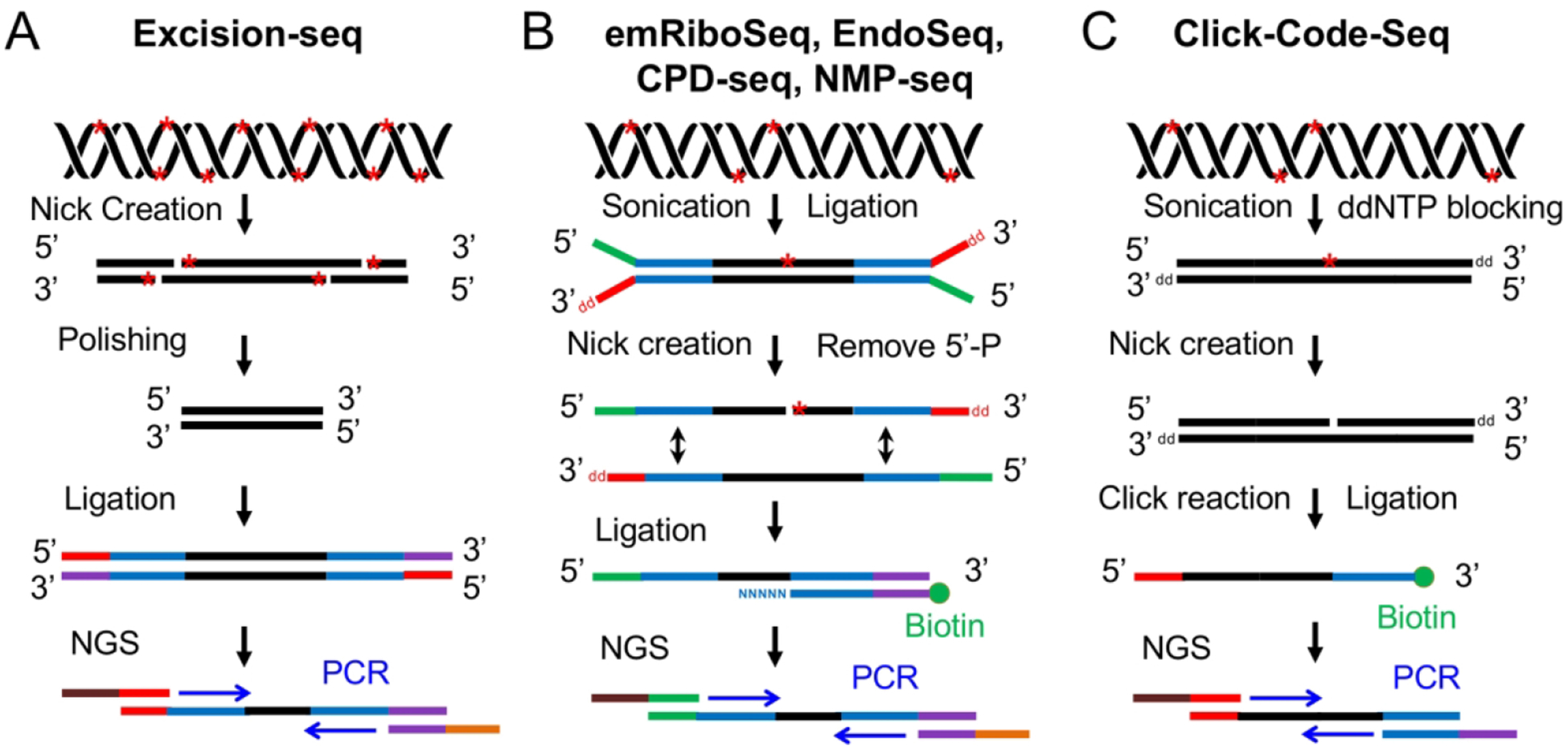
Schematic of six NGS-based methods using nick creation and ligation-based strategy for detection of DNA damage. (A) Excision-seq method for detection of uracil and UV damage indicated by red stars in DNA (Bryan et al. 2014). The UDG and Endo IV are used to digest uracil, and UVDE and photolyases are applied to nick at sites of UV damage. After polishing, adapter ligation and PCR amplification, the library is subjected to NGS. (B) Overview of experimental workflow for emRiboSeq, EndoSeq, CPD-seq, NMP-seq (Ding et al. 2015; Mao et al. 2016; Mao et al. 2017). After sonication and ligation, the DNA damage (red stars) are recognized and digested by specific repair enzymes to create a nick 5’ to the lesion. Then, the 5’-P group is removed and the second adapter is ligated to the DNA fragments containing 3’-OH group. Following ligation, the ligation products are amplified by PCR and subjected to NGS. (C) Click-Code-Seq method for detection of oxidative damage (Wu et al. 2018). After sonication and ddNTP blocking, one nucleotide gap is created by FPG and APE1 repair enzymes. Then, a prop-dGTP is incorporated to fill the gap and a 5’-azido-modified code sequence is ligated to the 3’ end by click reaction followed by the 5’ end adaptor ligation. The ligation products are amplified and sequenced by NGS.
