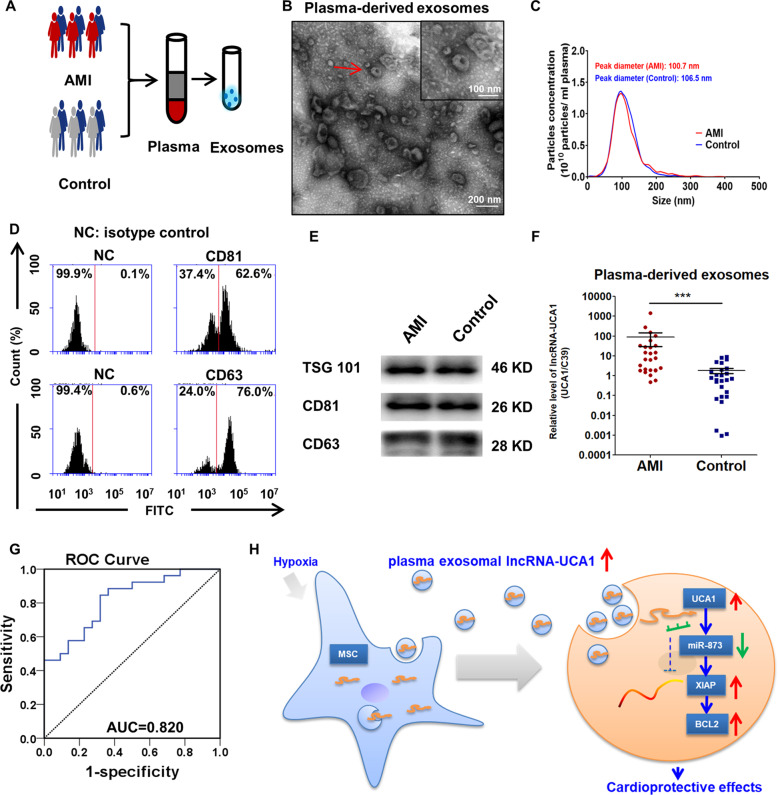
Fig. 8. Circulating exosomal lncRNA-UCA1 may be a promising novel biomarker for AMI diagnosis.
a Exosomes were isolated from the plasma of patients with AMI within 12 h or from healthy volunteers. b Representative electron micrograph of the extracted exosomes. Red arrows indicate plasma-derived exosomes. Scar bar: 100 nm. c Nanoparticle tracking analysis demonstrating size distribution of exosomes purified from AMI patients and healthy volunteers. X axis represents size of exosomes. Y axis represents the particle concentration in 1 ml PBS (before dilution). d Surface markers (CD63, CD81) of plasma exosomes were detected by flow cytometry. Exosomes that were not stained with CD63 or CD81 antibodies were labeled as NC group. e Western blots showing the protein levels of TSG101, CD63, and CD81 in plasma-derived Exo. f qRT-PCR analysis of UCA1 level in plasma exosomes from AMI patients (n = 26) and healthy volunteers (n = 26). Data are normalized to spiked cel-miR-39 (C39). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001. Statistical analysis was performed with Mann–Whitney U test. g The ROC curve for the diagnostic value of plasma-derived exosomal lncRNA-UCA1. (n = 52). h Exosomal lncRNA-UCA1 derived from hypoxic hMSCs promoted cell viability and attenuated apoptosis via miR-873-5p/XIAP/p-AMPK axis. Moreover, exosomal lncRNA-UCA1 in plasma may serve as a potential noninvasive biomarker for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI).