Figure 6. LYPLAL1 activation imparts metabolic benefits in vivo.
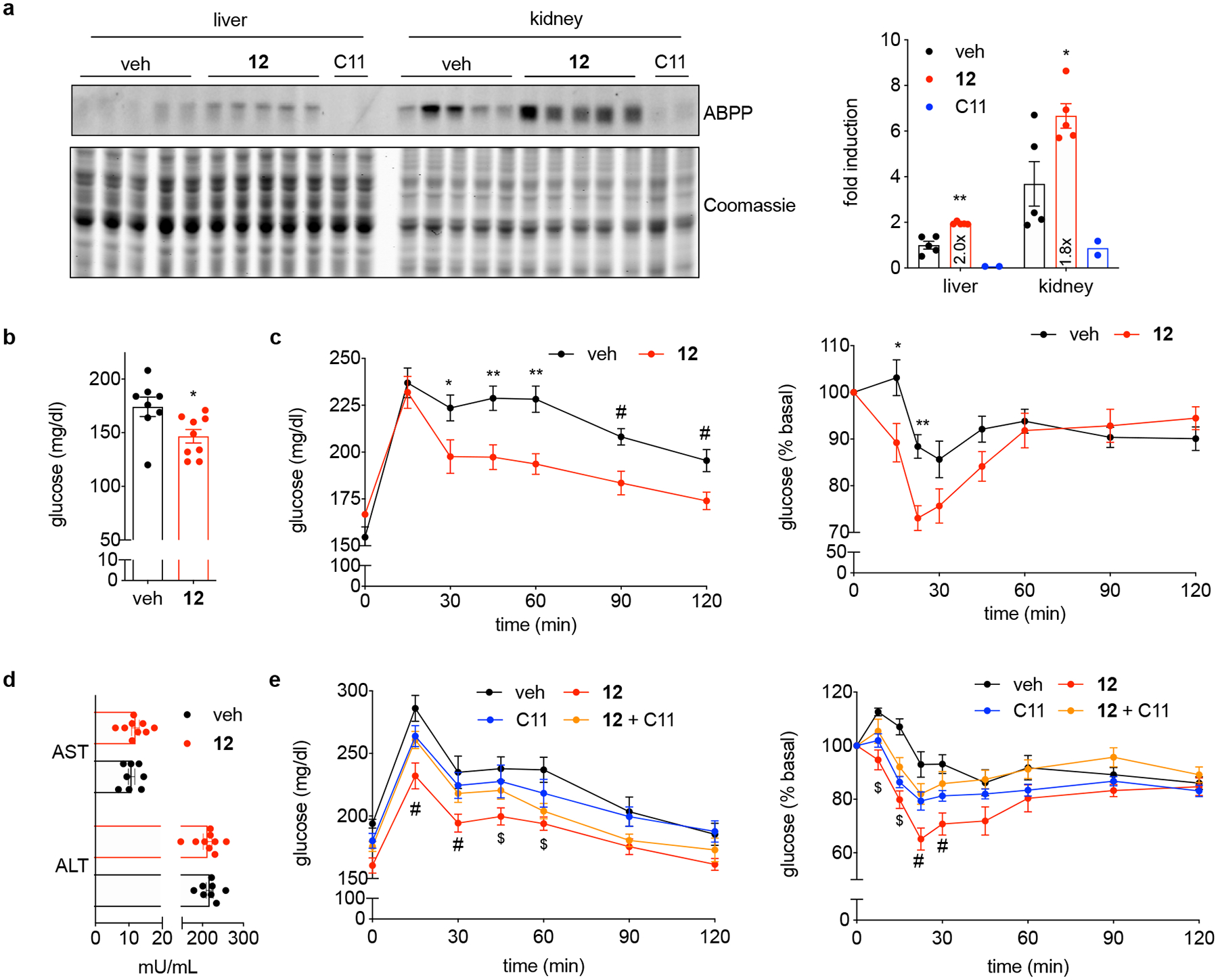
(a) 12 enhances LYPLAL1 activity in vivo. Mice were dosed with 12 or C11, a potent and selective LYPLAL1 inhibitor. Five minutes later, all mice were injected with a LYPLAL1-directed alkyne probe. Twenty minutes after the second injection, tissues were harvested, processed for click chemistry to attach an azide-rhodamine tag and analyzed by gel-based ABPP. Lanes represent individual mice. LYPLAL1 activity was quantified and expressed relative to the mean of activity in the liver of vehicle-treated mice (set to 1; n=5 for vehicle and compound 12, n=2 for C11). *p=0.02,**p=0.002 by two-tailed t-test. (b) Treatment with 12 corrects features of obesity-diabetes. DIO mice were dosed intraperitoneally with 12 (100 mg/kg every other day) and fasting glucose measured after 19 days. *p=0.02 by two-tailed t-test. (c) Glucose (left panel) and insulin (right panel) tolerance tests performed after 11 and 15 days of treatment, respectively, show 12 imparts metabolic benefits. For left panel: *p=0.04,**p<0.007 (0.006, 0.002) by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test; #p<0.02 (0.007, 0.01) by two-tailed t-test. For right panel: *p=0.01,**p=0.004 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. (d) ALT and AST plasma levels after 19 days of treatment. (e) Co-treatment of DIO mice with compound 12 and the LYPLAL1 inhibitor, C11 (5 mg/kg), reverses the beneficial effects of 12 on glucose tolerance (left panel, day 8 of treatment) and insulin sensitivity (right panel, day 12 of treatment). #p<0.041 by two-tailed t-test to all groups, $p<0.008 vs. vehicle by two-tailed t-test. Representative results from two (b-e) independent experiments; similar results were obtained in both experiments. Error bars represent (a-e) mean ± s.e.m.; (b-d) n=8 for vehicle- and n=9 for 12-treated mice, (e) n=7 for vehicle-, 12- and combination-treated mice, and n=8 for C11-treated mice where n represents individual mice. Uncropped gels/blots for a are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6.
