Extended Data Fig. 1. Screen to identify modulators of LYPLAL1 activity.
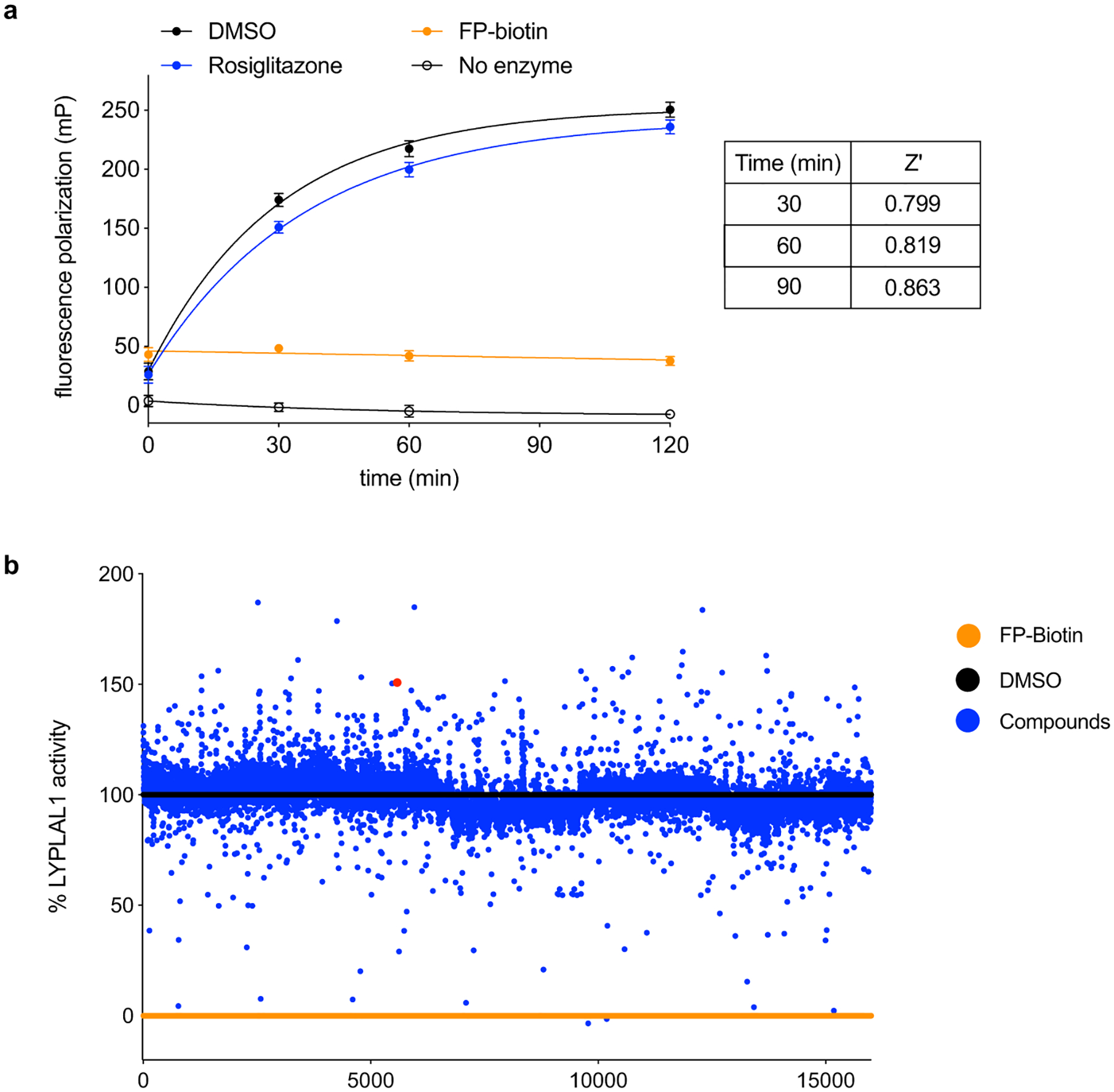
(a) ABPP-based fluorescence polarization assay (Fluopol-ABPP) amenable for high-throughput screening. Purified mLYPLAL1 is incubated with compounds prior to addition of the FP-rhodamine (FP-Rh) probe. FP-biotin probe (a non-fluorescent FP probe, 25 μM) serves as a control for inhibition, while the PPARγ ligand rosiglitazone (25 μM) is used as an inactive control. Data are shown as mean ± s.d., n=12, where n represents independent samples. (b) A 16,000-compound screen (single point, 10 μM) identified hits that reduced the fluorescence polarization signal of FP-rhodamine labeling of mLYPLAL1 (putative inhibitors) and some that increased it (potential activators). Percent mLYPLAL1 activity was calculated relative to DMSO (100% activity) and FP-biotin (0% activity) wells. 4 is shown as a red dot.
