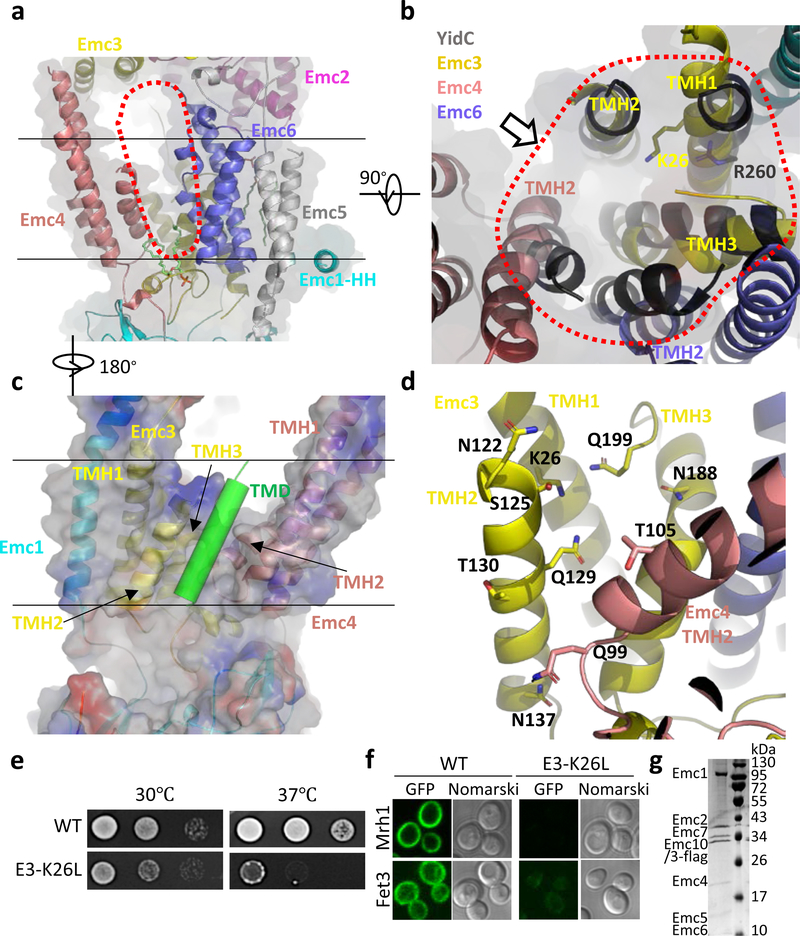
Fig. 3. The transmembrane region of the yeast EMC contains a client-binding pocket.
a, Structure of the transmembrane domain shown as a cartoon in front view. Two parallel black lines mark the lipid bilayer position. The red dots outline the elongated large cavity. Note the horizontal α-helix (HH) in Emc1 at the interface between the lumen and the membrane. b, Superposition of YidC (PDB ID 5Y83) as a black cartoon on the transmembrane domain of EMC in cytosolic view. The red dots encircle the five EMC α-helices aligned with YidC. The putative client TMD position is shown by the arrow, which is suggested by previous YidC-ribosome EM structure 22. c, A front view of the EMC transmembrane region in cartoon and surface potential. The green cylinder represents a client TMD located between TMH2 of Emc3 and TMH2 of Emc4 in the putative client binding pocket. Panels c and d are viewed from the back of panel a. d, The polar environment of the putative client binding pocket of the EMC. e, Two-day growth of 10-fold serially diluted cells (WT and Emc3-K26L mutant) on YPD plates at 30 °C and 37 °C. f, Diminished amount of two EMC clients (Mrh1 and Fet3) in cells containing the Emc3-K26L mutation. EGFP is inserted in the C-termini of these genes. g, The Coomassie blue–stained SDS-PAGE gel of the purified mutant EMC containing a K26L single mutation in Emc3. The experiments in panels e-g were repeated three times yielding similar results. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.