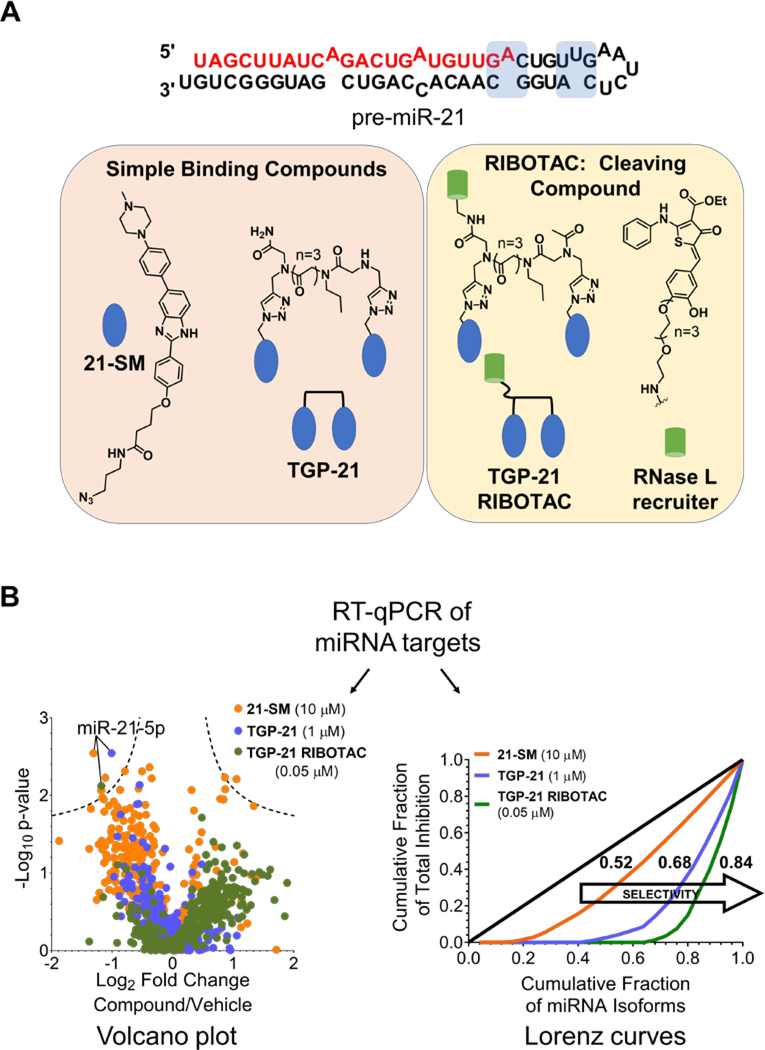
Figure 3.
Comparing the selectivity of a traditional small molecule, 21-SM, a dimeric compound with improved potency, TGP-21, and the nuclease recruiting TGP-21 RIBOTAC with Gini coefficients. A) Structure of the pre-miR-21 hairpin, where compound binding sites are highlighted in blue. Chemical structures of SMIRNA chemical probes 21-SM and TGP-21 and nuclease recruiting chemical probe TGP-21 RIBOTAC. B) RT-qPCR profiling data of chemical probes 21-SM (10 μM), TGP-21 (1 μM) and TGP-21 RIBOTAC (0.05 μM) in MDA-MB-231 cells shown as a Volcano plot. Gini coefficients and Lorenz curves calculated from the profiling data indicate selectivity for miR-21 increases in the following order: 21-SM < TGP-21 < TGP-21 RIBOTAC.