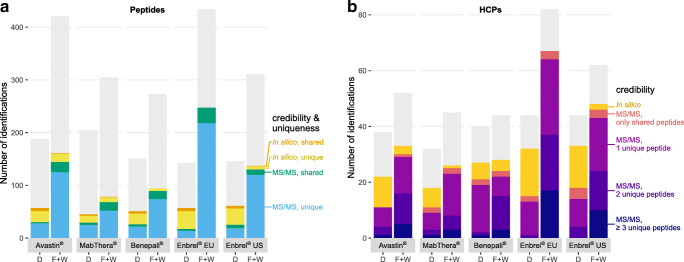
Fig. 2.
(a) Number of peptides and (b) number of proteins identified in the direct workflow (D) and in the combined flow-through and wash fractions of the depletion workflow (F+W) for each drug product. Each bar summarizes the results from three replicates (considering protein identification in one replicate sufficient). Colored bar sections highlight HCP-derived peptides and HCPs, respectively; moreover, they indicate credibility of detection and, in the case of peptides, their uniqueness. By contrast, light gray bars illustrate the total number of identified proteins or peptides, including putative contaminants (keratins) and “non-HCPs” (standard peptides, trypsin, protein A, drug products). “MS/MS” refers to identifications based on fragment ion spectra; “in silico” denotes identifications based solely on full-scan mass spectra. A peptide is considered “unique” if it matches a single sequence in the database; otherwise, it is classified as a “shared” peptide. Individual underlying peptide and HCP identifications are shown in ESM Fig. S3