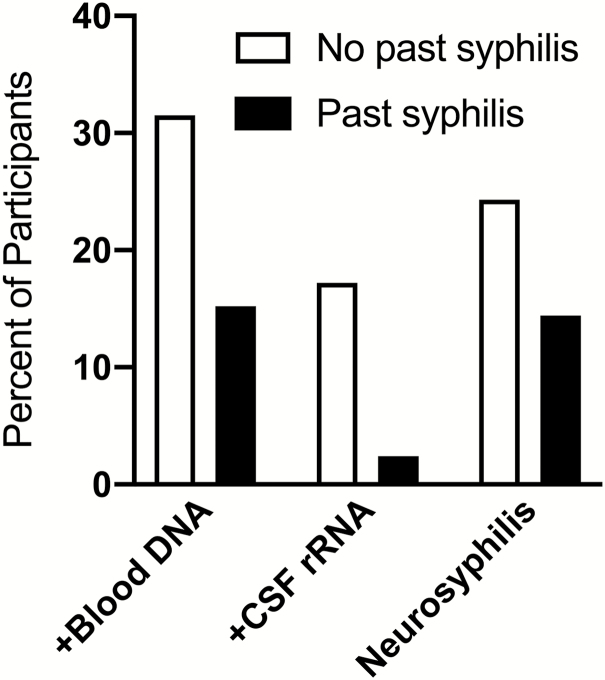
Figure 2.
Proportions of participants with and without previous syphilis who had detectable Treponema pallidum DNA in blood or rRNA in CSF or neurosyphilis at the index visit. Compared with individuals without previous syphilis, those with previous syphilis were significantly less likely to have detectable T. pallidum DNA in blood or rRNA in CSF (P < .001 for both), and they were significantly less likely to have neurosyphilis (P = .003). Neurosyphilis was defined as CSF white blood cells >20/uL or a reactive CSF-Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test. Abbreviation: CSF, cerebrospinal fluid.