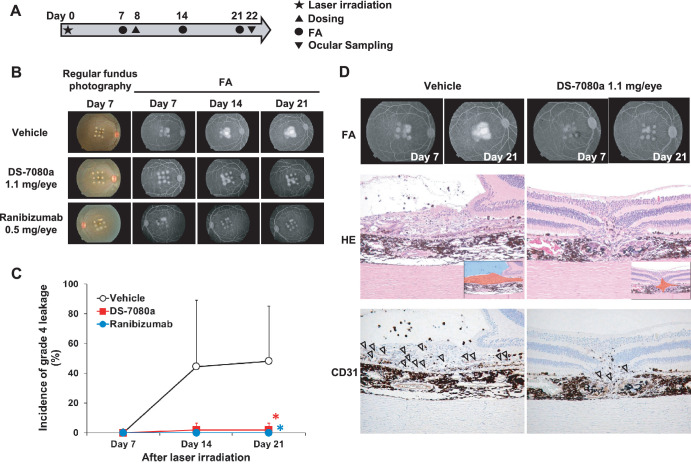
Figure 4.
DS-7080a reduces the incidence of neovascularization in a nAMD model in cynomolgus monkeys. (A) Dose, observation, and sampling schedule of the experiments in the choroidal neovascular model. Laser irradiation was performed 8 days prior to intravitreous dosing of DS-7080a and ranibizumab (day 0). DS-7080a (0.044, 0.22, and 1.1 mg/eye), ranibizumab (0.5 mg/eye), or vehicle were administered intravitreously to six eyes of three monkeys each (n = 6) on day 8. FA was carried out on day 7 (pre-dosing), day 14, and day 21. (B) The regular photography and FA of cynomolgus monkeys’ eyes in the CNV model. (C) The leakage of fluorescein in the lesion of laser injury was scored based on fluorescence FA using a blinded method according to the grading scale for CNV. The percentages of grade 4 leakage (bright hyperfluorescence early or mid-transit, with late leakage extending beyond the borders of the laser spot) were calculated, and the values for vehicle, ranibizumab, and 1.1-mg/eye of DS-7080a groups were plotted. Each point represents the mean ± SD (n = 6). Parametric Dunnett's test, *P < 0.05. (D) FA (days 7 and 21) of vehicle- and DS-7080a-treated eyes. Corresponding hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and CD31 staining images at day 22 (at the end of the study) are exhibited below. The insets in the H&E staining illustrate the proliferative lesion of choroid (red) and fluid accumulation (blue). Arrowheads indicate CD31-positive endothelial cells.