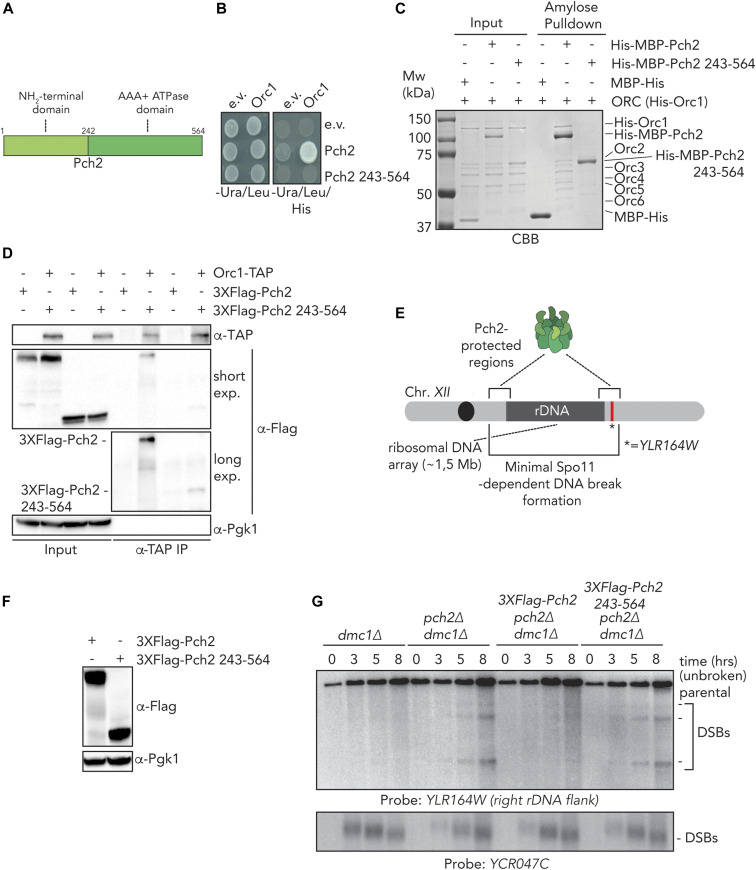
Figure 3. The NH2-terminal domain (NTD) of Pch2 is required for ORC–Pch2 formation.
(A) Schematic of Pch2 domain organization. (B) Yeast two-hybrid analysis between Orc1 and Pch2 (full-length Pch2, and AAA+ ATPase domain [Pch2-243-564]). (C) Amylose-based pulldown of His–ORC (His–Orc1-6) purified from insect cells, with His–MBP–Pch2 or His–MBP–Pch2-243-564. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation of 3xFlag-Pch2 and 3xFlag-Pch2 243-564 with Orc1–TAP (via α-TAP-IP) during the meiotic prophase (4 h into meiotic program). For α-Flag, short and long exposures are shown. α-Pgk1 is used as a loading control. (E) Schematic of the role of Pch2 in controlling Spo11-dependent DNA double-strand break (DSB) formation within the flanking regions of the budding yeast ribosomal DNA array located on chromosome XII. * indicates location of YLR164W locus, where DSB formation is interrogated. (F) Western blot analysis of meiotic time-course samples of yeast strains expressing wild-type 3xFlag-Pch2 and 3xFlag-Pch2 243-564 as used in (A). (3xFlag-PCH2 pch2Δ dmc1Δ and 3xFlag-pch2 243-564 pch2Δ dmc1Δ). (G) Southern blot analysis of YLR164W locus (right ribosomal DNA flank; chromosome XII) and YCR047C locus (control DSB region; chromosome III), in dmc1Δ, pch2Δ dmc1Δ, 3xFlag-PCH2 pch2Δ dmc1Δ, and 3xFlag-pch2 243-564 pch2Δ dmc1Δ background. dmc1Δ is a DSB repair deficient mutant used to detect accumulation of meiotic DSBs.