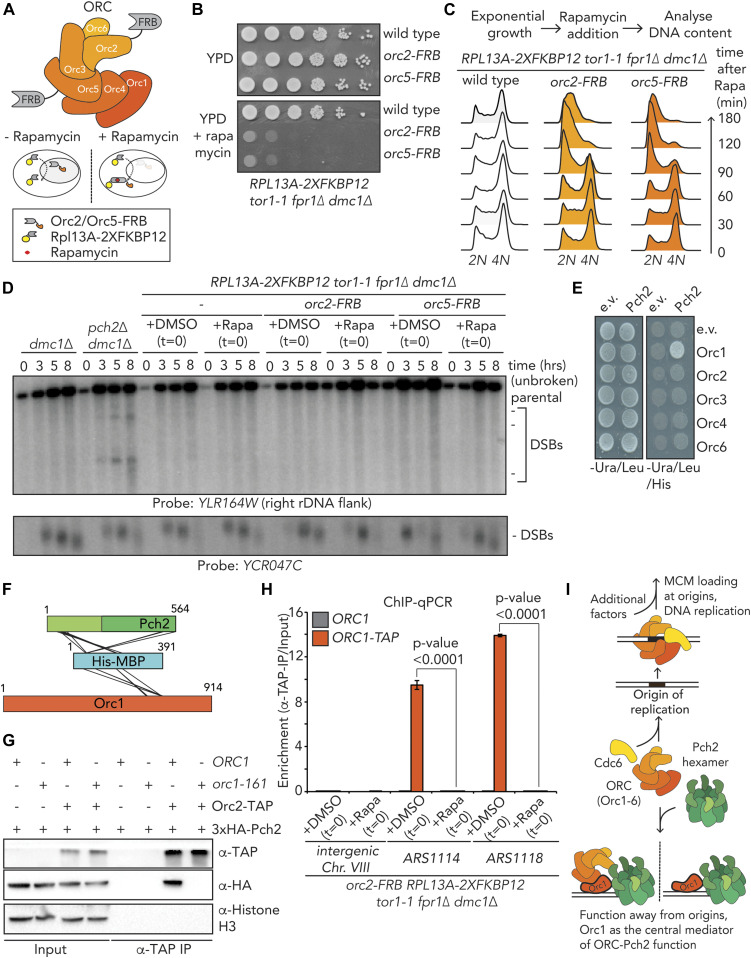
Figure 6. Functional in vivo analysis of origin recognition complex (ORC)–Pch2.
(A) Schematic of the ORC assembly and rapamycin-based anchor-away method. (B) 10-fold serial dilution spotting assay for anchor-away strains (untagged, orc2-FRB and orc5-FRB). Strains are grown on YP-dextrose (YPD) or YPD + rapamycin (1 μg/ml). (C) Flow cytometry analysis of efficiency of orc2–FRB and orc5–FRB nuclear depletion. Cells were treated as indicated, with rapamycin (1 μg/ml) at t = 0. (D) Southern blot analysis of YLR164W locus (right ribosomal DNA flank; chromosome XII) and YCR047C locus (control double-strand break [DSB] region; chromosome III). dmc1Δ is a DSB repair deficient mutant that is used to detect accumulation of meiotic DSBs. Rapamycin (1 μg/ml) or DMSO was added at indicated t = 0. Samples were taken at indicated time points after meiotic induction. (E) Yeast two-hybrid analysis between Pch2 and Orc1, Orc2, Orc3, Orc4, and Orc6. (F) Schematic indicating inter–MBP–Pch2 and inter–MBP–Orc1 nonredundant cross-links. (G) Co-immunoprecipitation assay of Pch2–E399Q with Orc2–TAP in ORC1 or orc1-161 backgrounds (via α-TAP-IP) during the meiotic prophase (4 h into meiotic program). Experiments were performed at 23°C. (H) TAP-based ChIP-qPCR in ORC1 and ORC1–TAP expressing orc2–FRB anchor-away strains. Rapamycin (1 μg/ml) or DMSO was added at t = 0, and samples were taken at t = 4 h. Primers that amplify Intergenic Chr. VIII (control locus), ARS1114, and ARS1118 were used. Experimental data are the average of three biological replicates. SEM is indicated. Significance was calculated using an unpaired t test, and P-values are indicated. (I) Model depicting the origin-independent function of Pch2–Orc1/ORC in local meiotic DSB control.