FIGURE 6.
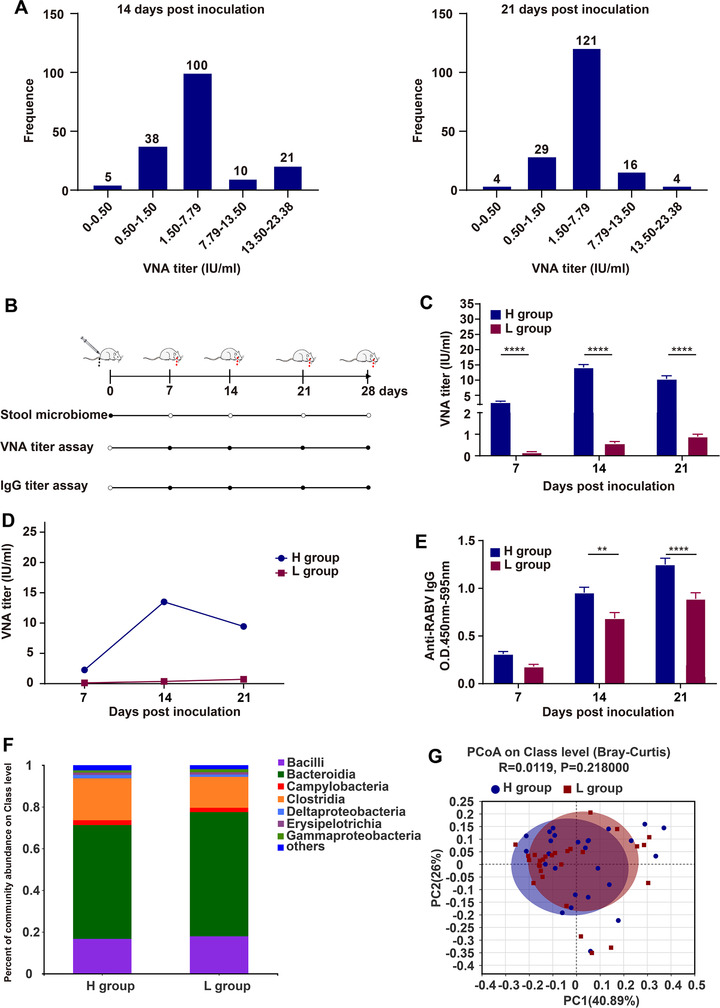
Gut microbiome composition is associated with anti‐RABV antibody production in the natural population of mice. A, Serum VNA titers in the natural population of mice immunized with rabies vaccines. Total 174 female ICR mice aged 6‐8 weeks were intramuscularly (i.m.) inoculated with 107 FFU iLBNSE in gastrocnemius muscle of the right hind limb, and VNA titers in the serum were measured by FAVN test at 14‐ and 21‐days post vaccination, respectively. B, Schematic of 16S rRNA screening. ICR mice were i.m. inoculated with 107 FFU iLBNSE. Then samples were collected and analyzed at regular intervals (black circles). C‐E, VNA and total IgG titers in VNA titer high (H) and low (L) group were determined by FAVN test and ELISA (H group, n = 26, L group, n = 26). The arithmetic mean of VNA titers (C), geometric mean of VNA titers (D), and total IgG level (E) was shown. Error bars represent standard error (** P < .01; **** P < .0001; Student's t‐test). F, Composition and relative abundance of gut microbiome at the class level. G, Principal coordinate analyses (PCoA) based on Bray‐Curtis illustrates the similarity of the fecal microbiota in H and L group
